How are continuous plastic products manufactured? A plastic extruder machine is crucial in transforming raw plastic materials into finished goods. This article will explain how these machines work, their main components, and their role in the manufacturing industry.
1、Plastic extruder machines transform various forms of raw plastic into continuous profiles through a combination of mechanical energy and heat, making them essential in the plastics manufacturing industry.
2、The main types of plastic extruder machines—single-screw and twin-screw—offer unique advantages, with single-screw extruders being cost-effective for simple profiles and twin-screw extruders providing enhanced mixing and production speed for more complex processes.
3、Choosing the right plastic material and machine, along with regular maintenance and best practices, is critical for optimizing production quality and efficiency in the plastic extrusion process.
Understanding Plastic Extruder Machines
Plastic extrusion is a manufacturing technique that produces continuous products with a uniform cross-section. At its core, the primary purpose of plastic extrusion is to manufacture continuous profiles from raw plastic, transforming various forms of plastic material—such as plastic pellets, plastic granules, flakes, and powders—into finished products.
The main function of a plastic extruder machine is to push or pull the raw material through a shaped die, using a combination of mechanical energy from screws and heaters to melt the plastic. Supporting this complex process is a range of auxiliary equipment, including precision feeders and cooling systems, which ensure high-quality outputs.
These systems work in harmony to maintain the efficiency and consistency of the extrusion process, making plastic extruders indispensable in the plastics manufacturing industry. Understanding the structural components and types of these machines reveals how they contribute to seamless plastic production.
Key Components of a Plastic Extruder Machine
The process involves several components:
- The heated barrel heats and softens the plastic before shaping.
- The feed throat channels plastic material from the hopper into the barrel, maintaining a steady flow.
- Once inside the barrel, the plastic is transported to the die through the feed pipe or adapter, where it will be shaped into the desired profile.
The screw diameters and length-to-diameter ratio are key to efficiently melting and proper mixing the plastic. Screw speed, typically ranging from 100 to 120 RPM, or up to 180 RPM in high-speed models, directly influences the output capacity.
The breaker plate functions as both a filter and a pressure maintainer within the barrel. The cooling system quickly solidifies the extruded material, finalizing the transformation from raw to finished product. These components collaborate to ensure high-quality plastic production.
Types of Plastic Extruder Machines
Plastic extruder machines come in various types, each designed to meet specific manufacturing needs. The main categories include single-screw, twin-screw, and ram extruders. While single-screw and twin-screw extruders are the most common, each type offers unique advantages tailored to different aspects of the plastic extrusion process.
The die mold used in these machines creates continuous profiles, which are essential for producing uniform plastic products. Understanding the specifics of single-screw and twin-screw extruders clarifies their roles.
Single-Screw Extruder Machines
A single screw extruder consists of a barrel. It features a single rotating screw inside. This design is particularly well-suited for producing simple profiles such as pipes and sheets, and it can process up to 100% recycled plastics. The energy efficiency of single-screw extruders ensures fast and gentle melting of materials, resulting in high-quality melts. Despite their benefits, these machines have limitations, such as slower speeds and less effective mixing capabilities compared to twin-screw extruders. The single extrusion head design contributes to these characteristics.
More cost-effective and reliable, single-screw extruders are popular among manufacturers. They excel in mass production of simple plastic products and are a staple in the industry. For more complex processing, twin-screw extruders are often the better choice.
Twin-Screw Extruder Machines
Twin-screw extruders contain two parallel screws within the barrel. Twin-screw extruders come in co-rotating and counter-rotating sub-types. These twin screw extrusion machines offer several advantages, including:
- Enhanced stability
- Improved mixing
- Increased production speed
- Efficient air and fume exhaustion They are particularly preferred for applications that require uniform mixing of materials.
Their flexible design permits the use of two or more extruders simultaneously, ideal for complex processes. This is particularly advantageous for applications requiring precise control, like producing high-quality plastic products. Twin-screw extruders are indispensable in the plastics manufacturing industry for their versatility and efficiency.
The Plastic Extrusion Process
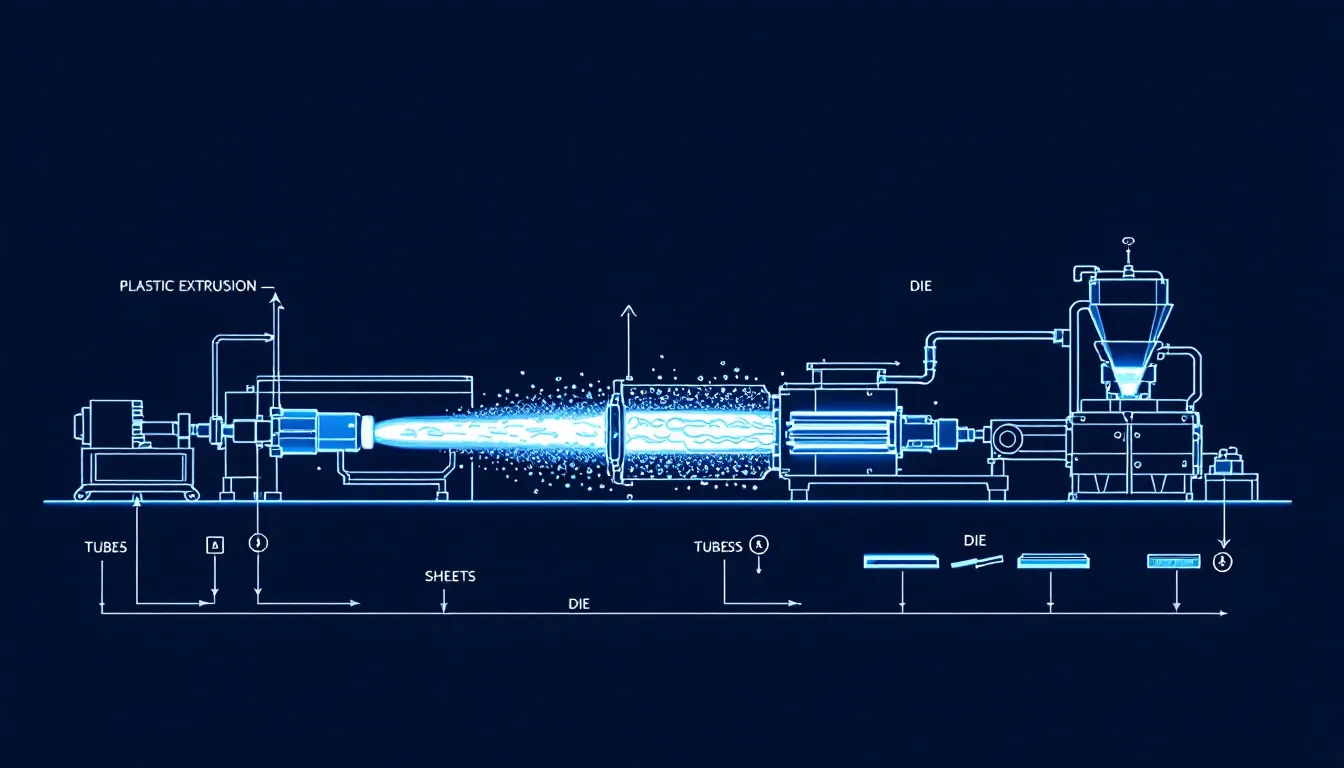
Plastic extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process for creating continuous shapes from melted thermoplastic materials. The process involves:
- Feeding thermoplastic material through a hopper into the extruder.
- Using a rotating screw in the extruder to generate pressure and push melted plastic through a die.
- Melting the material as the screw rotates and heating elements apply heat to push and heat the material.
Once melted, the material is filtered through a screen pack to remove contaminants before shaping in the melting process. The die used in the extrusion process determines the final shape and cross-section of the extrudate.
The extrusion process involves:
- Cooling the extruded product using water baths or cooling rolls to solidify it.
- Maintaining a consistent temperature profile along the extruder barrel to ensure optimal processing and product quality.
- Using auxiliary equipment like precision feeders and cooling systems to support the process and ensure high-quality outputs.
Material Selection for Plastic Extrusion
Choosing the right plastic material is key to the final product’s quality and functionality. Common plastic materials for plastic extrusion include:
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene
- Polyacetal
- Acrylic
- Nylon
- Polystyrene
- PVC
- ABS
- Polycarbonate Each plastic type has unique properties that affect extrusion performance.
The Melt Flow Index (MFI) indicates how well a plastic flows under heat, influencing shape complexity. Polyethylene and other semi-crystalline polymers crystallize at the frost line during cooling, affecting the polymer melt, melt temperature, and molten plastic as well as molten polymer during processing.
Colorants and UV inhibitors can be mixed with resin before extrusion to modify the final product’s properties. Selecting the right material ensures extruded products meet desired specifications and performance standards.

Specialized Plastic Extrusion Techniques
Specialized techniques like co-extrusion and compounding extrusion create products with multiple material layers and enhanced properties. These often require twin-screw extruders for compounding capabilities.
We’ll explore two specific techniques: tubing extrusion and blown film extrusion.
Tubing Extrusion
Tubing extrusion produce pipes and tubing for industries like automotive, plumbing, and packaging. It involves:
- Using jacketing tooling for coating wires and wire insulation
- Employing equipment and techniques that ensure uniform flow and shape
- Maintaining precise temperature and pressure control
The uniform temperature and flow are critical for achieving high-quality tubing products. Proper cooling systems and downstream equipment are crucial for maintaining steady volumetric throughput and tubing integrity in a continuous process.
Tubing extrusion’s versatility enables complex shapes and internal cavities, making it valuable in plastics manufacturing.
Blown Film Extrusion
Blown film extrusion produces food packages, shopping bags, and continuous sheeting. The process involves:
- Drawing and blowing the film, resulting in thinner thickness than the extruded tube and aligning polymer chains.
- Cooling the melt before it leaves the die to form a weak semi-solid tube.
- Further processing the semi-solid tube.
An annular die ensures uniform thickness and improved film quality. Cooling leads to the crystallization of semi-crystalline polymers, affecting the final product’s properties.
Blown film extrusion is crucial for producing high-quality plastic film for packaging.
Advantages of Using Plastic Extruder Machines
Plastic extruder machines are essential in plastics manufacturing due to several advantages. They allow for high production rates and the rapid production of uniform products. Their versatility enables the production of continuous and complex shapes like pipes and profiles, including plastic extrusion machines, extrusion machines, and plastic extrusion equipment.
Single-screw extruders are cost-effective due to their reliability and lower operational costs. Overall, plastic extruder machines offer significant benefits in efficiency, design versatility, and cost-effectiveness.
These advantages make plastic extruders a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, driving innovation and productivity.
Challenges and Solutions in Plastic Extrusion
Plastic extrusion, like any manufacturing process, faces challenges. Common defects include:
- Surface texture, such as melt fracture caused by excessive shear stress from temperature or speed issues
- Dimensional inconsistencies, or surging, which can result from feeding problems, worn components, or temperature discrepancies
- Structural weaknesses
Bubbles and voids in extrusions often result from moisture in the material, vaporizing during processing and creating gas pockets. Regular die cleaning prevents defects like die lines from surface damage or contamination. Implementing best practices and promptly addressing issues significantly improve plastic extrusion quality.
Applications of Plastic Extrusions
Plastic extrusions are widely used due to their versatile properties and applications. In construction, extruded plastics are used in products like windows and doors, contributing to energy-efficient designs. The automotive industry uses plastic extrusion for plastic parts like weather seals, gaskets, and interior trims, enhancing durability.
The packaging industry uses plastic extrusion to create films and plastic sheets and plastic sheeting with varying thicknesses and barrier properties, enhancing protection and shelf life. Medical device manufacturing benefits from plastic extrusion for complex profiles in tubing and catheters, ensuring regulatory compliance in industrial applications with different viscous plastics. The plastics industry plays a crucial role in these processes.
The versatility and customization of plastic extrusions and custom shapes make them indispensable across multiple sectors.
Choosing the Right Plastic Extruder Machine
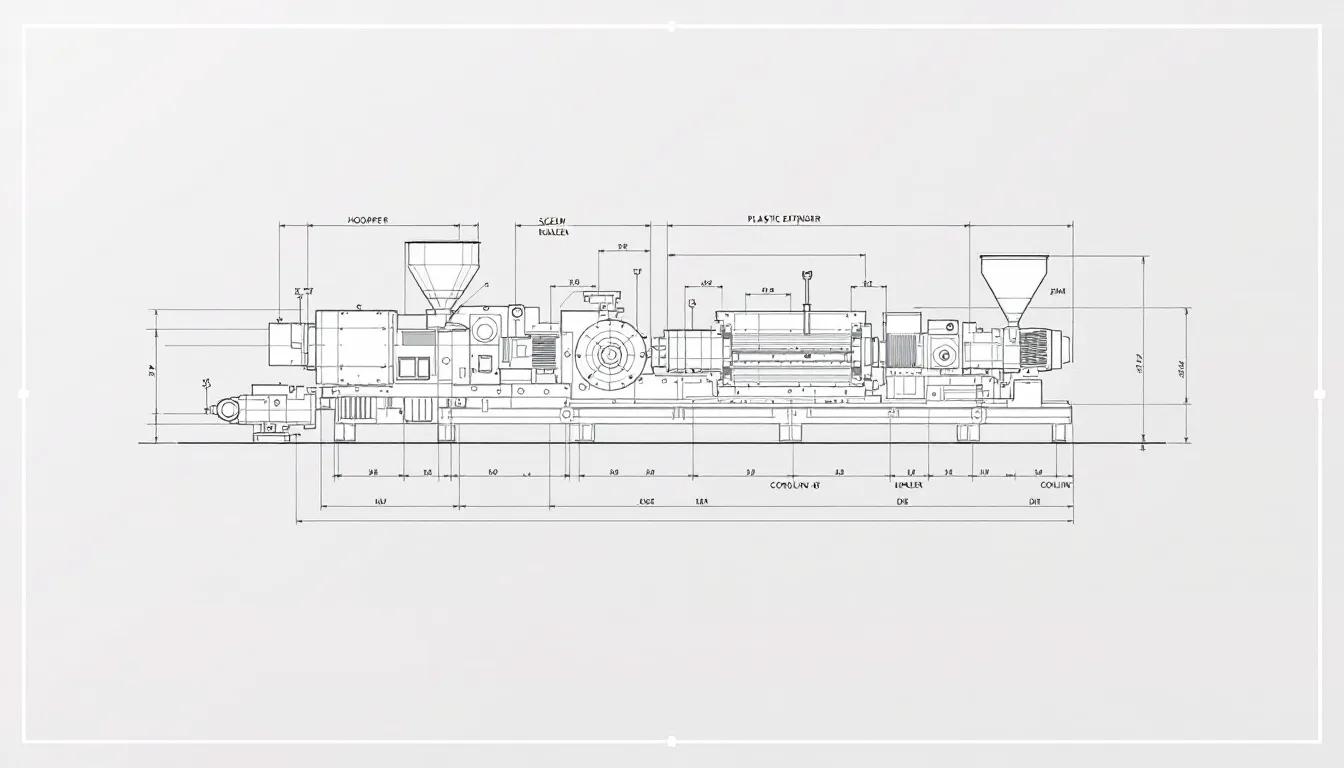
Choosing the right plastic extruder machine optimizes production and ensures product quality. Material compatibility with additives maintains the base materials’ properties during extrusion. Understanding material-specific shrinkage and warping is key to achieving precise dimensions in extruded products.
Key considerations for extrusion include:
- Thermal stability during extrusion to prevent material degradation.
- Considering material viability and availability to aid in effective production.
- An extruder’s barrel having multiple temperature control zones for uniform melting and minimal degradation.
The right extruder enhances production speed and reduces waste, improving overall product quality.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Tips for Plastic Extruder Machines
Regular maintenance and calibration ensure dimensional accuracy during the extrusion process. Manufacturer reputation and after-sales service are critical, as reliable support minimizes downtime and enhances performance. Most plastic extrusion issues stem from material properties, temperature control, and pressure settings.
Proper cooling and pulling setups are essential, as uneven cooling can cause warping. Implementing these tips helps maintain efficiency and quality, ensuring consistent plastic extrusion standards.
Summary
Plastic extruder machines play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing, offering efficiency, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding the different types of extruders, their components, and the extrusion process itself is crucial for optimizing production and ensuring high-quality outputs. Material selection and specialized techniques further enhance the capabilities of these machines, making them indispensable across various industries.
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, it’s evident that plastic extruders are more than just machines—they are the backbone of countless products that improve our daily lives. By leveraging the knowledge shared in this guide, you can make informed decisions, troubleshoot effectively, and maintain your extruder machines for optimal performance. Embrace the potential of plastic extrusion and drive innovation in your manufacturing processes.




