Key Takeaways
- Plastic extrusion is a precise manufacturing process that transforms thermoplastic materials into various shapes through heating, melting, and cooling.
- Understanding the types of extruders—single screw and twin screw—is crucial for selecting appropriate equipment for specific applications, with each type offering distinct advantages.
- Custom and co-extrusion techniques allow for the production of tailored plastic profiles and multi-layered structures, enhancing product performance and meeting diverse industry needs.
Understanding Plastic Extrusion
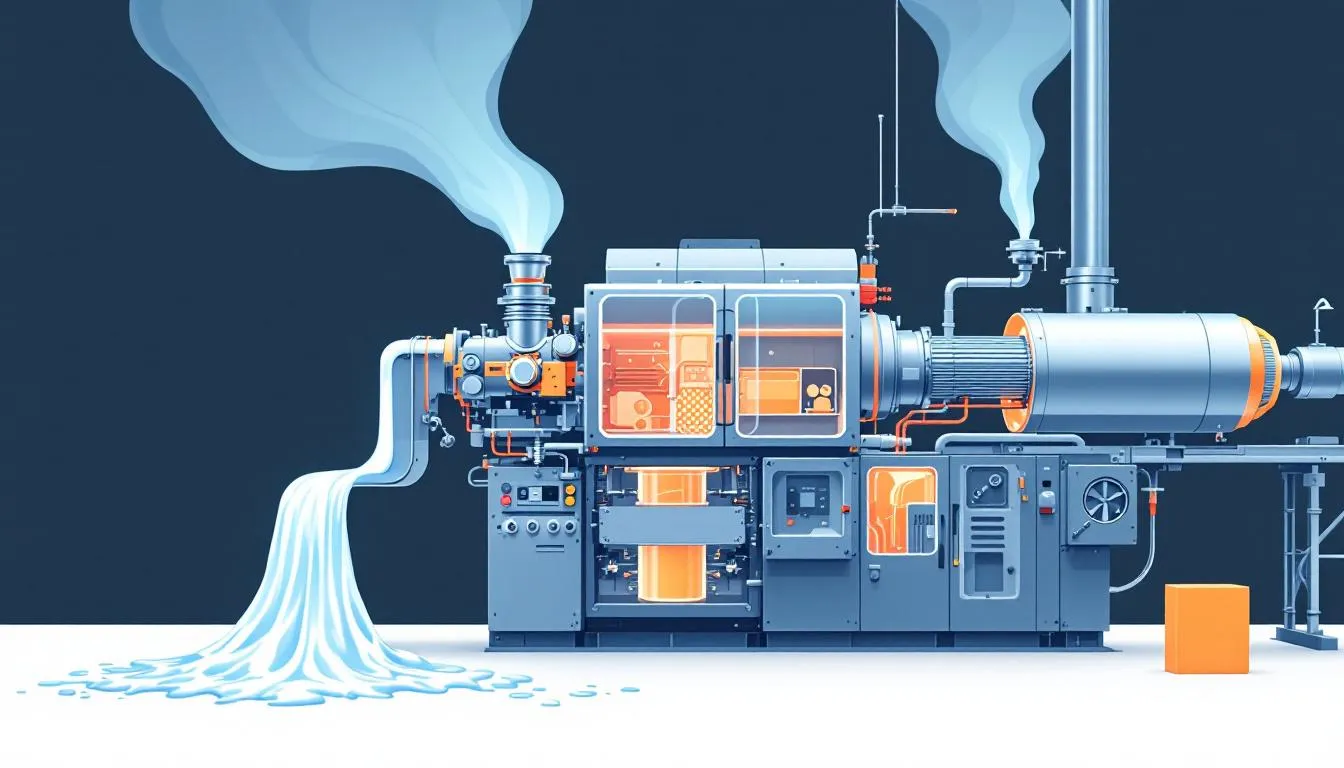
Plastic extrusion is a method where thermoplastic material is melted into a homogeneous state before being shaped through a die. The process involves the following steps:
- Feeding raw plastic material from a hopper into the barrel.
- Inside the barrel, a rotating screw applies pressure, pushing the molten plastic through a precisely shaped die, which determines the final profile of the extruded product.
- Cooling the extruded material to retain its newly formed shape.
Picture a bustling factory floor where the plastic extrusion process is in full swing:
- Raw plastic granules are fed from a hopper into the barrel.
- The granules are heated and transformed into a molten polymer.
- The rotating screw applies just the right amount of pressure to push the molten plastic through the die.
- The extruded plastic profiles emerge and are quickly cooled.
- The profiles solidify into their final shapes, showcasing various plastic forming processes in the high volume manufacturing process, including profile extrusion.
This process is not just about turning plastic into usable forms; it’s about precision and efficiency. Each step, from feeding the raw material to cooling the extruded product, is meticulously controlled to ensure high-quality results. Whether it’s producing stock plastic extrusions or custom plastic profiles, the plastic extrusion process is a marvel of modern manufacturing.
Key Components of Plastic Extruders
Understanding the key components is essential to appreciate the intricacies of plastic extrusion. Central to the process is the plastic extruder, a machine with several critical parts. The hopper stores raw plastic granules, which are then transported into the heated barrel through the feed throat.
Inside the barrel:
- The rotating screw heats and melts the plastic.
- The breaker plate filters the molten plastic and maintains the necessary pressure within the barrel.
- The molten plastic eventually reaches the annular dies, shaping the material into the desired profile, passing through the screen pack.
Think of the plastic extruder as a well-orchestrated symphony. The components work together to create a seamless extrusion process:
- The hopper and feed throat supply raw material steadily.
- The barrel and rotating screw melt and push the plastic forward in harmony.
- The breaker plate filters and maintains pressure.
- The die shapes the molten plastic into intricate profiles.
These components yield high-quality extruded plastic products with remarkable precision.
Types of Plastic Extruders
Plastic extrusion features two primary types of extruders: single screw and single extrusion head twin screw extruders. Single screw extruders are ideal for processing uniform materials, making them popular in the food and packaging industries due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
Twin screw extruders excel in mixing and processing complex materials, offering precise control over material blending to create products with specific characteristics. They are commonly used for advanced plastic applications that require high precision and consistency.
Imagine a scenario where a manufacturer needs to produce a high-volume batch of plastic film for food packaging. A single screw extruder would be the go-to choice, offering a cost-effective and straightforward solution. However, for a project requiring intricate blending of different viscous plastics, a twin screw extruder would be indispensable, ensuring the final product meets exacting standards.
Recognizing the differences between these individual extruders delivering helps manufacturers select the right tool for the job, ensuring optimal performance and quality.
Materials Used in Plastic Extrusion

Plastic extrusion’s versatility comes from the wide range of thermoplastic materials it can utilize. Common materials include:
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) for its strength and ease of molding
- Polycarbonate for its impact resistance and optical clarity
- High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS), which combines standard polystyrene’s properties with enhanced toughness, increasing its resilience.
Materials and their valued properties:
- Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG): valued for clarity, toughness, and recyclability; commonly used in packaging.
- Polyurethane: renowned for elasticity and durability.
- Rigid Polyvinyl Chloride (RPVC): preferred for strong, durable plastic profiles.
- Nylon (a type of polyamide): favored for strength and heat resistance; popular in demanding applications.
Additives can enhance these materials’ properties, making them more durable, flame-resistant, or UV-protected. This flexibility allows manufacturers to tailor the extrusion process to meet specific needs, from flexible packaging to rigid structural components. Choosing the appropriate materials and additives allows manufacturers to create extruded plastic profiles that adhere to the highest standards of performance and quality.
Custom Plastic Extrusions
Custom plastic extrusion provides numerous possibilities for businesses producing unique products tailored to niche market demands. The process can create various shapes, including custom shapes and extruded profiles:
- Sheets
- Tubes
- Custom profiles designed to meet project needs Custom extrusion’s flexibility allows for quick and cost-effective solutions, making it attractive for many industries.
Materials in custom extrusion can be tailored for specific needs, such as UV protection and custom color concentrates. Co-extrusion of multiple materials is also possible, allowing for even more customization. A reliable manufacturer should offer capabilities like tooling design and build, prototyping, and all secondary operations to ensure quality and efficiency.
Consider a company needing a custom plastic profile with specific UV resistance for outdoor use. The manufacturer designs the tooling and prototypes the product in its desired form, ensuring it meets all aesthetic requirements before full-scale production. This customization allows them to create profiles that not only meet but exceed expectations, providing unique advantages and a competitive edge in the market.
Co-Extrusion Techniques
Co-extrusion involves the simultaneous extrusion of multiple material layers using two or more extruders. This process bonds different plastics into layered structures without mixing them, enhancing the final product’s performance characteristics through plastic co extrusion.
Co-extrusion is ideal for efficiently producing various products like sheets, tubes, and seals in large quantities. For instance, food packaging films often require multiple layers, each serving a different protective function. One layer might provide moisture resistance, while another offers chemical resistance, all achieved through co-extrusion.
Consider a packaging manufacturer’s production line in the packaging industry. Multiple extruders feed different materials into a single extrusion line, creating multi-layered plastic film. Each layer is carefully controlled to provide specific properties, resulting in a product that meets stringent industry standards. Co-extrusion enhances product performance and enables innovative solutions to complex manufacturing challenges.
Secondary Processes and Finishing Options
Secondary processes and finishing options are crucial for achieving the desired quality and functionality of extruded plastic products. Techniques like CNC trimming precisely shape plastic parts by removing excess material through programmed routes in manufacturing processes. Fastening techniques like screws and rivets attach plastic components without heat, ensuring strong and stable assemblies.
Ultrasonic welding and heat staking join plastic components by applying high-frequency vibrations or localized heat and pressure to fuse parts together. Decorative techniques like pad printing can apply multiple colors to complex plastic surfaces, enhancing the final product’s aesthetic appeal.
A cooling system quickly solidifies the extruded plastic product after it passes through the die, ensuring dimensional stability and quality. These secondary processes and finishing options turn raw extrusions into finished products that meet high standards of precision and performance, including the use of air cooling rolls.
Applications of Plastic Extrusions
Plastic extrusions have varied applications, just like the materials and techniques used to produce them. Their durability makes plastic extrusions resistant to corrosion, moisture, and chemicals, suitable for harsh conditions like those in the construction and automotive industries. Their insulating properties enhance energy efficiency, benefiting building designs.
Plastic extrusion is widely used to create weather stripping, fencing, and wire insulation, essential components in various industries. The process can produce both flexible and rigid products, suitable for applications including medical tubing and adhesive tapes. The lightweight properties of plastic extrusions make handling, transport, and installation easier, broadening their range of applications.
Consider the versatility of plastic extrusions in everyday life. From the weather stripping that insulates your home to the medical tubing that saves lives, their impact is profound. Industries like automotive, building and construction, and agriculture rely on these durable and versatile products to meet specific needs.
Benefits of Using Plastic Extrusions
Plastic extrusions offer numerous and compelling benefits. The process is cost-effective for large-scale production, allowing continuous runs once the initial tooling is established. Compared to alternatives like metal or wood, plastic extrusion generally offers lower production costs, making it economically viable for many industries.
Plastic extrusion is known for:
- Its efficiency, enabling rapid production of both simple trim pieces and complex dual-layered tubes.
- Minimizing waste, making it an environmentally friendly manufacturing option.
- Its versatility, allowing for a wide variety of customized shapes, sizes, colors, and finishes to meet diverse market demands in plastics extrusion.
Picture a production line churning out thousands of components with minimal waste and maximum efficiency. Each piece is precisely shaped and customized to meet specific requirements, from simple trim pieces to complex multi-layered tubes. The efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits of plastic extrusion make it a preferred choice for manufacturers globally.
Choosing the Right Plastic Extrusion Manufacturer
Selecting the right plastic extrusion manufacturer is crucial for your project’s success. Key considerations include material selection, assessing a supplier’s capabilities to ensure their offerings match your project requirements. Maintaining effective communication with the supplier to reduce production disruptions. Enhancing overall project management through collaboration.
Knowing pricing structures and contract terms early prevents unexpected manufacturing experience costs. Choosing a manufacturing partner with extensive experience and a proven track record ensures your plastic extrusion needs are met with high standards of quality and efficiency.
Summary
In summary, plastic extrusion is a versatile and efficient manufacturing process that transforms raw plastic material into a wide array of products. From understanding the basic principles to exploring advanced techniques like co-extrusion, we’ve covered the key components, materials, and benefits of plastic extrusions. Whether you’re in the automotive, construction, or agriculture industry, plastic extrusions offer durable, cost-effective, and customizable solutions.
As you consider your manufacturing needs, remember the importance of selecting the right plastic extrusion manufacturer. With the right partner, you can achieve high-quality results that meet your specific requirements and exceed your expectations. Embrace the possibilities of plastic extrusion and discover how it can elevate your projects to new heights.
]]>Key Takeaways
- Recycled plastic extruders convert waste plastics into reusable materials, playing a critical role in sustainability and reducing environmental waste.
- Key components, such as the hopper, barrel, and screws, are essential for the efficient operation of recycled plastic extruders, facilitating the transformation of plastics into high-quality products.
- Choosing the right recycled plastic extruder involves considering processing capacity, energy costs, and the specific types of plastics it can handle, ensuring optimal efficiency and effectiveness in recycling operations.
Understanding Recycled Plastic Extruders

Recycled plastic extruders are pivotal in the fight against plastic waste. These plastic recycling machines transform discarded plastics into reusable materials, playing a vital role in supporting sustainability and cost-effectiveness. The process involves converting scrap plastic into high-quality pellets, which can then be used in various manufacturing processes, thereby reducing environmental waste.
Recycled plastic extruders work by heating, compressing, and shearing plastic, allowing it to be reshaped into new products. Repurposing plastic waste with these machines significantly reduces landfill contributions, tackling one of today’s major environmental challenges.
Plastic waste is first collected and sorted by type and quality. These sorted plastics are then fed into the extruder for transformation. This not only supports environmental sustainability but also showcases the potential of plastic recycling technologies in creating new products from what was once waste.
Key Components of a Recycled Plastic Extruder
Key components of a recycled plastic extruder include the hopper, which acts as the entry point for plastic feedstock. The barrel houses the screws and controls the temperature, ensuring the plastic is adequately melted for further processing.
Heaters provide the thermal energy needed to melt the plastic inside the barrel. The screws, considered the heart of the extruder, move, compress, and mix the plastic, ensuring it reaches a uniform molten state.
The molten plastic then reaches the die, which shapes it into its final form. A cooling system solidifies the melted plastic upon exiting the die, ensuring it retains the desired shape. These components are vital for efficiently transforming plastic waste into valuable products.
How Recycled Plastic Extruders Work
The operation of recycled plastic extruders starts with shredding the collected plastic waste, increasing its surface area for efficient melting. The shredded plastic is then heated within the extruder barrel, converting it into a molten state for further processing.
Advanced filtration systems remove contaminants from the molten plastic, ensuring high-quality end products that are manufactured. The molten plastic is then shaped through moulds, which define the final form, dimensions, and characteristics of the extruded product.
The extrusion process involves the following steps and outcomes:
- After shaping, the extruded plastic product is rapidly cooled to maintain its form.
- The process enables the creation of various products, including pellets and sheets, from recycled plastic.
- Once cooled, the solidified plastic can be cut or further processed for other applications.
This highlights the versatility and efficiency of this recycling method.
Benefits of Using Recycled Plastic Extruders

Recycled plastic extruders offer numerous benefits, making them indispensable in modern recycling processes:
- They help recycle materials, significantly reducing plastic pollution.
- Manufacturing recycled plastic products locally decreases transportation emissions, further reducing plastic pollution.
- US manufacturers adhere to strict environmental standards, minimizing pollution.
Modern plastic extrusion machinery is designed to optimize energy consumption, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Recent legislative changes are promoting the use of recycled materials in plastic production, boosting demand for energy-efficient practices. Using recycled plastic extruders enhances material efficiency, resulting in less raw material waste during production.
These machines conserve resources and support sustainable practices by reducing waste and promoting energy efficiency. Their role in recycling processes is essential for creating a more sustainable and efficient future, highlighting the importance of environmental stewardship.
Applications of Recycled Plastic Extruders

Recycled plastic extruders have a wide range of applications across various industries. In the automotive industry, they are used to create parts like door seals and bumper components, which need to withstand wear and environmental conditions. In the medical field, extruded plastic provides components like IV tubing and catheters that require sterility and chemical resistance.
Consumer packaging also benefits from plastic extrusion, resulting in lightweight and hygienic containers that help preserve product quality. In the construction industry, plastic extrusion is widely utilized for making durable plastic materials like PVC pipes and window frames. These applications demonstrate the versatility and durability of products created through plastic extrusion.
Household items such as storage containers and decorative trims are often produced using plastic extrusion. Innovative technologies like CPM Extricom Extrusion recycle PET waste into material suitable for food-grade applications, overcoming challenges like moisture content. The RingExtruder RE® from CPM offers enhanced control over the recycled product’s color, crucial for applications requiring aesthetic consistency. Additionally, polyethylene terephthalate is a key material in the production of these containers.
These examples highlight the extensive and impactful use of recycled plastic extruders in various sectors.
Choosing the Right Recycled Plastic Extruder for Your Needs
Choosing the right recycled plastic extruder ensures maximum efficiency and meets specific needs. Consider factors like intended use, processing capacity, and storage capacity of output bales. Machine throughput and capacity determine its efficiency, with options ranging from small-scale operations processing 20-50 kg per hour to large-scale operations handling up to 2,200 kg/h.
Key considerations include:
- Energy costs, representing around 10-20% of overall production expenses.
- Raw material costs, comprising 50-70% of total expenses.
- Ensuring the machine can process specific types of plastics with particular resin codes, such as PET, to align with your intended application. Raw materials play a crucial role in determining overall production efficiency.
For small-scale recycling machines, prioritize ease of use, security measures, and low noise levels. Evaluating these factors carefully helps businesses select the most appropriate and efficient extrusion machine for their recycling needs.
Maintenance Tips for Recycled Plastic Extruders
Regular maintenance ensures the longevity and efficiency of recycled plastic extruders. Key maintenance practices include:
- Inspecting and lubricating moving parts regularly to minimize wear and tear.
- Scheduling routine maintenance checks to identify potential issues before they escalate.
- Keeping detailed maintenance logs to track the extruder’s performance and servicing history.
To maintain optimal operating conditions and ensure consistent high-quality production, it is important to:
- Monitor temperature and pressure settings regularly.
- Inspect the screw and barrel for wear or damage.
- Assess output quality to detect deviations in product specifications.
To maintain the extruder properly:
- Clean the extruder thoroughly after each production run to prevent material contamination.
- Use compatible cleaning agents to help maintain the machine’s integrity.
- Identify abnormal noises or vibrations early, as they can indicate mechanical issues needing attention.
Following the manufacturer’s guidance for troubleshooting specific extruder problems ensures effective maintenance.
Cost Considerations for Recycled Plastic Extruders
Financial considerations are crucial when investing in recycled plastic extruders:
- Initial costs for small models can range from $10,000 to $30,000.
- Larger models can cost between $90,000 and $200,000.
- Choosing energy-efficient machinery can substantially reduce operational expenses and lessen environmental impacts, making them a wise long-term investment.
Electricity usage during shredding or crushing significantly affects operating costs. Maintenance costs typically amount to about 5-10% of the equipment’s cost each year, and labor costs should be considered if the extruder is not self-built.
Budget considerations are crucial when selecting recycling machines, as they represent a significant investment. Understanding and planning for these costs allows businesses to make informed decisions, balancing initial investment with long-term operational savings.
Case Studies: Successful Use of Recycled Plastic Extruders

Real-world examples of recycled plastic extruders in use can provide valuable insights and inspiration. For instance, Prad and Lala from Chennai, India, use their extrusion machine to make furniture, demonstrating practical and creative possibilities. Joop from Haute Plastique in Rotterdam creates sleek, aesthetically pleasing products from recycled materials, showcasing the machines’ potential.
Businesses worldwide are successfully using recycled plastic extruders to turn waste into valuable products. These case studies illustrate the transformative impact of these machines, highlighting their versatility and effectiveness in various business applications.
Summary
Recycled plastic extruders play a pivotal role in addressing plastic pollution by transforming waste into valuable products. Their benefits extend beyond environmental sustainability, offering energy efficiency and cost savings for businesses. The diverse applications of these machines across industries, from automotive to medical to consumer packaging, showcase their versatility and importance.
Proper maintenance and understanding cost considerations are essential for maximizing the efficiency and longevity of recycled plastic extruders. The success stories from around the world highlight the potential of these machines to revolutionize plastic recycling and contribute to a sustainable future.
As we continue to innovate and adopt sustainable practices, recycled plastic extruders will remain at the forefront of the fight against plastic pollution. Let’s embrace these technologies and work towards a greener, cleaner planet.
]]>Key Takeaways
- Leading manufacturers such as Coperion, Leistritz, and KraussMaffei Berstorff emphasize quality and innovation in plastic extrusion, catering to various industrial needs.
- Understanding the types of plastic extruders, including single and twin screw extruders, is essential for selecting the appropriate machinery for specialized applications.
- Recent advancements in plastic extrusion technologies focus on sustainability and energy efficiency, driving the industry towards improved production practices and environmental responsibility.
Leading Plastic Extruder Manufacturers
Choosing the right plastic extruder manufacturer is crucial for maintaining quality and reliability in your production line. Among the leaders in this field, Coperion stands out for its precision-engineered twin screw extruders, renowned for their high throughput and exceptional mixing capabilities. Coperion’s commitment to innovation makes them a go-to choice for many industries.
Equally prominent, Leistritz offers versatile twin screw extruders that cater to a wide range of applications, including pharmaceuticals and food. Their machines are designed for flexibility and efficiency, making them suitable for various complex extrusion processes.
Another key player, KraussMaffei Berstorff, specializes in extrusion technology for industries such as pipe and profile extrusion, demonstrating their extensive expertise in the field.
These manufacturers stand out due to their dedication to quality and innovation. Companies like Davis-Standard and Amut S.p.A. offer comprehensive extrusion solutions across multiple sectors, underscoring the importance of choosing a partner with a proven track record.
From the innovative Kneading Disc Technology of BUSS AG to the century-long experience of the Reifenhäuser Group, these manufacturers epitomize excellence in the plastics industry.
Types of Plastic Extruders
Knowing the various types of plastic extruders helps in selecting the right machinery for your needs. Single screw extruders are the workhorses of simpler extrusion processes, primarily melting and conveying materials to form basic shapes. These individual extruders are ideal for producing straightforward profiles where complex mixing is not required, especially when using a single extrusion head.
Twin screw extruders, on the other hand, are ideal for high-speed production and superior mixing capabilities. Their modular screw design allows for easy customization, making them suitable for a variety of applications, from consumer goods to industrial components. One screw counter-rotating twin screw extruder and rotating screw are particularly efficient for shaping operations involving shear-sensitive materials, providing a tailored solution for specific needs.
Co-extruders enhance versatility by processing different materials simultaneously, creating multi-layered products with varied properties. This capability is particularly useful in applications requiring distinct material characteristics, such as barrier properties in packaging films or multi-functional profiles in construction. The ability to process multiple materials concurrently highlights the adaptability and efficiency of modern extrusion lines, especially when utilizing two or more extruders, including individual extruders delivering co extrusion.
Custom Plastic Extrusion Solutions
Custom plastic extrusion provides unmatched flexibility, enabling businesses to create unique designs with specific cross-sections and wall thicknesses. This is particularly beneficial for industries that require specific shapes and sizes that stock plastic extrusions cannot provide. Whether you need complex profiles or simple custom shapes, custom plastic extrusion can meet your exact specifications, including extruded plastic profiles.
A key advantage of custom plastic extrusion is its cost-effectiveness, particularly for medium to high-volume manufacturing processes. By leveraging custom solutions, businesses can achieve quick turnaround times and enhanced functionality, often integrating features like snap-fits to reduce assembly steps. This streamlines manufacturing processes and enhances product performance.
Additionally, the variety of thermoplastic materials available in custom extrusion solutions meets specific needs like flame resistance and chemical compatibility. Companies that excel in customization offer tailored solutions to meet unique project specifications, providing secondary processes like notching, drilling, and heat welding to enhance the final product. Custom plastic profiles can be designed to fit unique applications, ensuring that every detail aligns with your requirements. Custom fabrication can also play a crucial role in achieving these tailored solutions.
Advanced Plastic Extrusion Technologies
Advanced plastic extrusion technologies have revolutionized the industry, enhancing efficiency and sustainability in production processes. Modern extrusion lines feature energy-efficient drive systems that significantly reduce energy consumption, aligning with the industry’s push towards sustainability. These technologies not only lower operational costs but also minimize the environmental impact of manufacturing, particularly in the context of an extrusion line.
Automation and digital technologies lead this transformation, facilitating real-time monitoring and adjustments to maintain product quality and consistency. Automated monitoring systems are integral in modern plastic sheet extrusion lines, enhancing efficiency and ensuring that the final products meet stringent quality standards. Closed-loop systems further optimize material flow, facilitating precise control over the extrusion process.
Precision engineering improvements allow manufacturers to achieve tighter tolerances and better surface finishes on extruded products. Advanced simulation tools are now being used to optimize design and production processes, reducing development time and improving product quality. The integration of these technologies ensures that modern extrusion lines are capable of delivering high-quality products efficiently.
Materials Used in Plastic Extrusion
Material selection in plastic extrusion is crucial for attaining the desired properties in the final product. Common thermoplastic materials and plastic materials include:
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): widely used for pipes, films, and electrical wire insulation due to its excellent formability and durability.
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET): offers unique benefits (not specified in the text).
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS): offers unique benefits (not specified in the text).
ABS, known for its strength and flexibility, finds applications in automotive and consumer goods where these properties are essential. Polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene are also popular choices, particularly in packaging and consumer goods, due to their versatility and ease of processing. Material selection is often based on the specific requirements of the application, such as chemical resistance, impact strength, and thermal stability.
Materials like polycarbonate and nylon (polyamide) are selected for their unique properties. Polycarbonate is valued for its impact resistance and optical clarity, making it suitable for products like eyewear lenses and safety equipment. Nylon’s strength and heat resistance make it ideal for various industrial applications.
The diverse range of available materials ensures that plastic extrusion can meet the demands of virtually any industry.
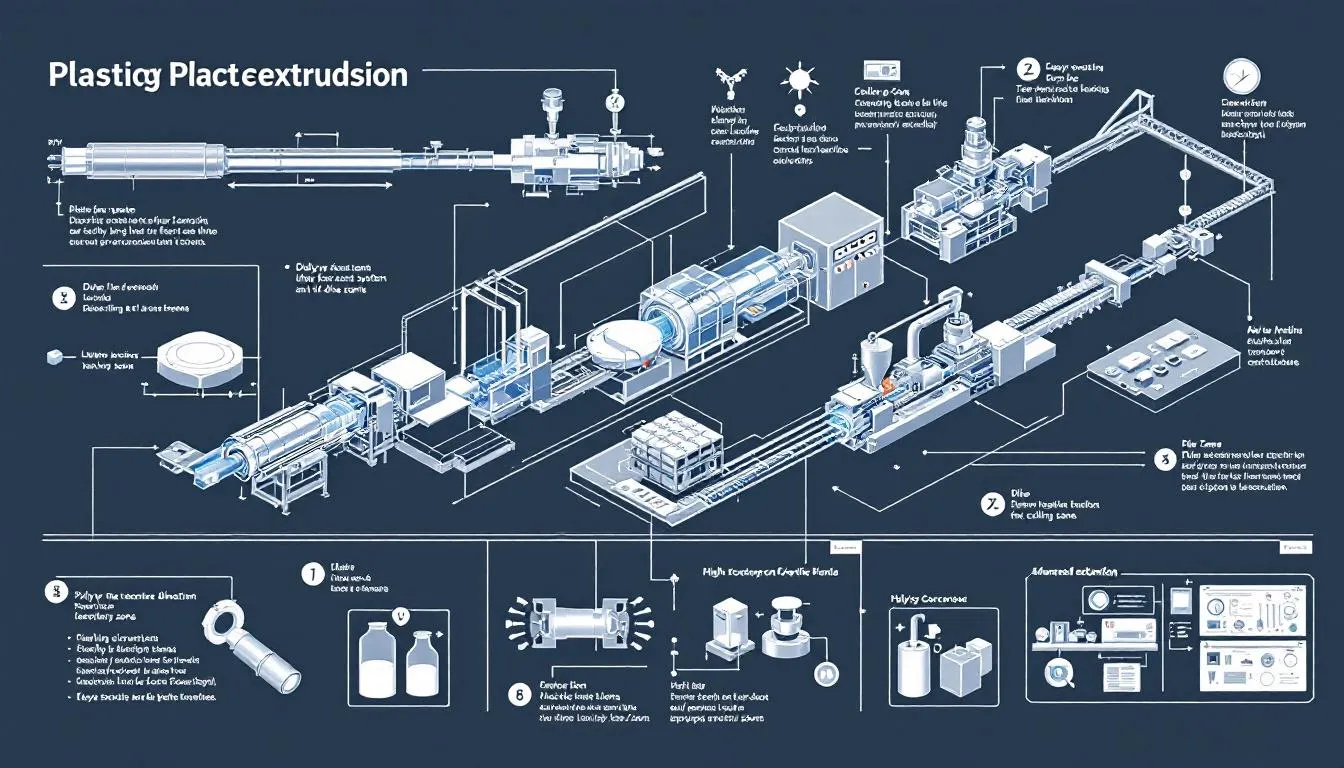
The Plastic Extrusion Process
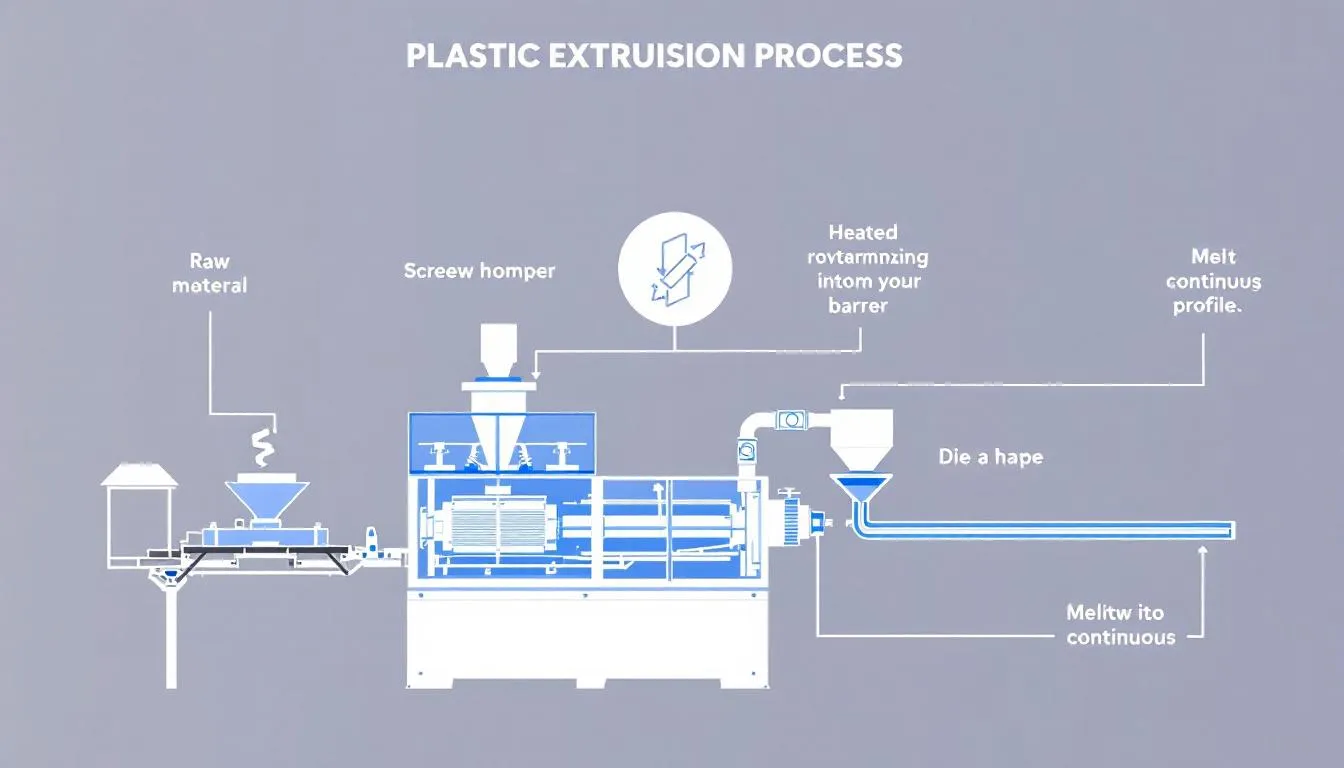
Plastic extrusion is a continuous, high-volume manufacturing process that shapes raw thermoplastic materials into specific forms through various plastic forming processes. The process includes the following steps:
- Introduction of thermoplastic raw material into the extruder via a hopper.
- Heating the material to a specific melt temperature within the heated barrel.
- Melting facilitated by friction and pressure inside the barrel. Plastics extrusion is an essential technique in this context, including plastic co extrusion.
The plastic extrusion process involves the following steps:
- Once the plastic material is in a molten state, it is filtered through a screen pack to remove any contaminants before being shaped into its final shape.
- The design of the die through which the molten plastic passes determines the shape of the extruded product.
- Cooling methods, such as water baths or cooling rolls, are employed to solidify the extruded profiles, ensuring that they maintain their form and dimensional stability.
Real-time monitoring and in-line inspection are essential for ensuring consistent material flow and high-quality production runs. Specialized machinery plays a vital role in maintaining the efficiency, production speed, and quality of the plastic extrusion process.
The versatility of extrusion allows for the creation of products that can be used as-is or further fabricated into complex assemblies, such as pipes, tubing, and plastic films.
Applications of Plastic Extrusions
Plastic extrusions are essential in numerous industries due to their versatility and durability. In the packaging industry, materials such as High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) are used to create plastic film and sheets that enhance product protection and extend shelf life. These extruded materials are essential for consumer goods and food packaging, providing both strength and recyclability.
In the medical field, plastic extrusion is crucial for producing compliant tubing and complex components like catheters, which are essential for various medical devices. The automotive industry also benefits significantly from plastic extrusions, using them to manufacture parts such as weather seals, gaskets, and fluid transfer tubing due to their chemical resistance and durability.
Construction applications include the use of extruded plastics for windows and doors, contributing to energy efficiency and quick installation. The solar industry leverages plastic extrusion to produce components like frames for solar panels, enhancing durability and longevity. These diverse applications underscore the integral role of plastic extrusions in modern industry.
Benefits of Working with Top Manufacturers
Partnering with leading plastic extruder manufacturers offers numerous advantages, ensuring efficient and reliable production processes:
- Top manufacturers operate their machinery continuously, minimizing the risk of inventory shortages.
- Continuous operation ensures steady production.
- This continuous operation is crucial for maintaining supply chain stability and meeting high-volume demands.
Access to innovative solutions in production techniques is another key benefit, providing unique advantages. Experienced manufacturers can create complex shapes and customized features, offering tailored solutions for specific needs. Additionally, reputable manufacturers offer engineering support to optimize the design and efficiency of the extrusion process, ensuring that every product meets high-quality standards.
Quality standards are crucial when selecting a manufacturing partner. Leading manufacturers adhere to:
- Strict quality controls, including relevant ISO certifications, ensuring product reliability and performance without compromising quality
- Strong after-sales support
- Transparent communication, ensuring that any issues are promptly addressed and resolved
How to Choose the Right Manufacturer
Choosing the right plastic extruder manufacturer requires careful consideration of several factors. Here are some steps to help you in the process:
- Utilize directories of leading extruded plastics manufacturers to compare their capabilities and offerings.
- Use this comparison to identify manufacturers that can meet your specific needs.
- Determine whether you require standard profiles or customized solutions to guide your selection.
Request samples helps evaluate the quality of a manufacturer’s products. Samples provide a tangible representation of the manufacturer’s capabilities and allow you to assess whether their products meet your desired form and material selection criteria. This due diligence ensures that you choose a manufacturing partner who can deliver high-quality, reliable extrusions for your applications.
Future Trends in Plastic Extrusion
The future of plastic extrusion is driven by advancements in sustainability, energy efficiency, and precision. The use of recyclable materials is becoming increasingly prevalent, promoting eco-friendly manufacturing practices. This shift towards sustainability is driven by the growing demand for environmentally responsible production methods.
Technological advancements, including automated monitoring and closed-loop systems, are revolutionizing the plastic extrusion industry. These technologies enable real-time adjustments and enhance production efficiency, ensuring steady volumetric throughput and consistent quality.
Energy efficiency and precision engineering will continue to drive innovation in the plastics industry, setting new production standards.
Summary
Plastic extrusion is a dynamic and essential process in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. Understanding the capabilities of top manufacturers, the types of extruders available, and the advanced technologies driving the industry is crucial for making informed decisions. From the materials used to the applications of extruded products, every aspect of plastic extrusion plays a vital role in achieving high-quality outcomes.
As the industry continues to evolve, embracing sustainability and technological advancements will be key to staying ahead. By partnering with reputable manufacturers and leveraging innovative solutions, businesses can ensure that they remain competitive in an ever-changing market. The future of plastic extrusion holds exciting possibilities, paving the way for more efficient, sustainable, and high-quality production.
]]>Key Takeaways
- Extruded plastic profiles are vital in various industries such as automotive, medical, and construction, providing functionality and design versatility.
- Customization in plastic extrusion allows for tailored profiles that meet specific industry requirements, enhancing functionality and precision.
- The plastic extrusion process involves careful quality control and monitoring to ensure optimal performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards.
Overview of Extruded Plastic Profiles

Plastic extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process that transforms raw plastic materials into continuous profiles, known as extruded plastic profiles and stock plastic extrusions. These profiles are indispensable in various industries, contributing significantly to manufacturing efficiency and versatility. From automotive parts to consumer goods, extruded plastic profiles are everywhere, enhancing both functionality and design.
The versatility of extruded plastic profiles is evident in their usage across diverse sectors:
- In the automotive industry, they are used for weather seals and interior trims.
- In the medical field, they form the backbone of tubing and catheters.
- Agricultural applications, consumer goods, and even solar panels benefit from the adaptability and durability of extruded plastic profiles.
The process allows for the manufacture of tailored shapes and manufactured components, ensuring that each profile meets specific industry requirements.
Common shapes of plastic profiles include:
- Thin films
- Rods
- Wire sheets
- Trims
- Channels
- Tubing
- Gaskets
These shapes are designed to meet the unique demands of their respective applications, providing durability, flexibility, and efficiency. Materials like polyacetal, acrylic, and nylon further expand the range of applications, making polymer plastic extrusion a versatile and invaluable process in modern manufacturing.
Types of Plastic Materials Used in Extrusion
The choice of plastic materials is crucial in plastic extrusion, as it determines the properties and applications of the final product. A variety of thermoplastic materials are utilized, including ABS, PVC, and polypropylene, each offering unique plastic material properties that cater to specific needs, including different viscous plastics. For instance, material selection is important, as PVC is known for its durability and resistance to environmental factors, making it ideal for construction and automotive applications.
Polyethylene, polypropylene, polyacetal, acrylic, nylon, polystyrene, ABS, polycarbonate, and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene are among the most commonly used materials in plastic extrusion. Each material brings its own set of advantages:
- Low density polyethylene: valued for its flexibility and resistance to chemicals.
- Polypropylene: offers high tensile strength and is used in a variety of industrial applications.
- Polycarbonate: known for its impact resistance and is often used in safety and electronic applications.
Bausano extruders, for instance, can process a wide range of materials, including PVC and HDPE, enhancing the possibilities for custom plastic extrusions. This capability allows manufacturers to select the best material for their specific application, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Custom Plastic Extrusions
Customization in plastic extrusion is a game-changer, allowing manufacturers to design unique profiles that meet specific industry requirements. This capability is especially crucial for projects that demand tailored solutions. Whether it’s a complex automotive component or a specialized medical device, custom plastic extrusions can be meticulously designed to enhance functionality and fit precise application needs.
The ability to produce small, tailored batches efficiently has significantly improved with advancements in customization capabilities. This means that even niche applications can benefit from the precision and versatility of custom plastic extrusions. Options for additive customization, such as UV resistance, color matching, and flame retardance, further enhance the performance of these profiles in various environments.
Precision manufacturing is key in custom plastic extrusions. Tolerances for wall thicknesses can range from 0.030 inches to 0.375 inches, ensuring that each profile meets the exact specifications required for its application. This high degree of customization in shapes and sizes makes extruded plastic profiles indispensable for a wide range of industries.
The Plastic Extrusion Process
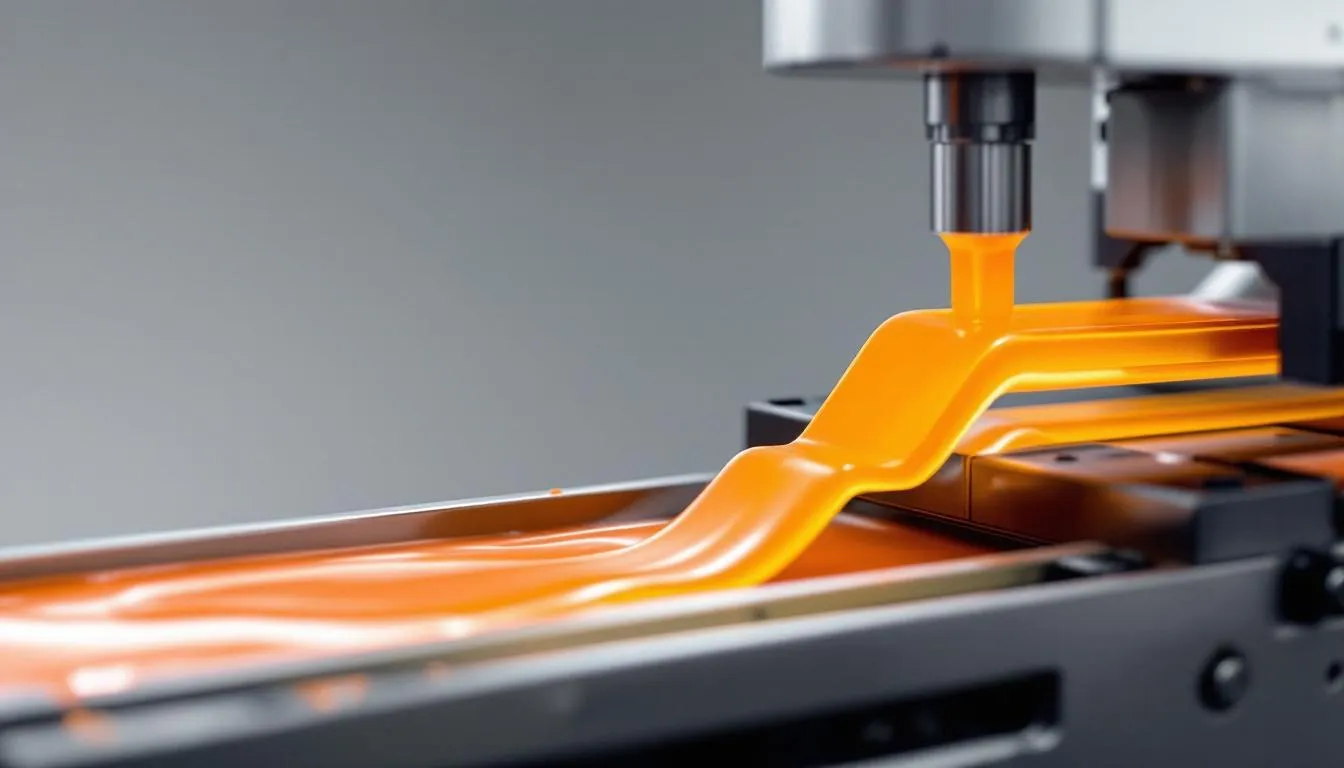

Plastic extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process that transforms raw plastic materials into continuous profiles. The processed materials involve:
- Starting with raw plastic materials, typically in the form of granules, plastic pellets, pellet form, or powder.
- Feeding these materials into a heated chamber.
- Using a rotating screw to move the materials through the chamber.
- Gradually melting the materials through friction and applied heat in the plastics extrusion process.
The extrusion process involves the following steps:
- The temperature applied is carefully tailored to the specific type of plastic being used.
- As the plastic moves through the screw conveyor, it is sheared and heated, eventually becoming molten plastic.
- This molten plastic is then forced through a die, which shapes it into the desired profile extrusion by extruding it.
- The design of the die is crucial, as it ensures a smooth and consistent flow of melted plastic into the final product shape.
Cooling is an essential part of the extrusion process. Once the plastic exits the die, it must be cooled quickly to retain its shape. This can be done using air or water as the extruded plastic moves onto a conveyor belt. Cooling rolls may also be used to cool and size the extruded plastic immediately, ensuring precise internal and external dimensions.
Quality control is integral to the plastic extrusion process. It involves:
- Assessment of raw plastic materials to ensure their purity and integrity.
- Regular inspection of the extrusion die and screw to maintain proper material flow and pressure.
- Monitoring temperature, pressure, and speed during the extrusion process to guarantee consistent product quality.
Applications of Extruded Plastic Profiles
Extruded plastic profiles are used in a wide range of applications, thanks to their versatility and functionality. In the construction industry, extruded profiles contribute to the creation of weather-resistant and thermally efficient profiles used in windows and doors. These profiles help improve energy efficiency and durability in buildings, making them an essential component in modern construction.
The automotive industry relies heavily on extruded plastic profiles for various parts, especially those such as weather seals and interior trims. These other components are designed to withstand chemical and temperature variations, ensuring long-lasting performance.
In the medical field, plastic extrusion is key for producing rigid tubing and catheters, utilizing medical-grade plastics that comply with regulatory standards.
Extruded plastics also play a significant role in the packaging industry, where they are used to create plastic film and sheets of various thicknesses. These materials offer protective qualities that enhance product shelf life. Additionally, materials like polycarbonate and polystyrene are used in specialized applications, such as electronic housings and solar panel frames, further showcasing the versatility of extruded plastic profiles.
Advantages of Using Extruded Plastic Profiles

The advantages of using extruded plastic profiles are numerous. Their lightweight nature simplifies handling, transportation, and installation, leading to significant cost savings. Additionally, extrusion tooling is generally more economical and efficient compared to other plastic manufacturing methods.
Plastic extrusions are also known for their resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and moisture, making them suitable for harsh environments. The fabrication process is straightforward, allowing for efficient cutting, drilling, and assembly. Twin screw extruders, in particular, offer enhanced efficiency and energy-saving benefits, especially when handling materials with poor thermal stability.
Twin Screw Extruders vs. Single Screw Extruders
Twin screw extruders and single screw extruders each have their unique advantages and applications. The most common type of twin screw extruders are divided into two main types. These are co-rotating and counter-rotating extruders. They excel in blending and reactive extrusion due to their advanced mixing capabilities. Moreover, twin screw extruders have superior venting and self-cleaning functions compared to their single screw counterparts.
Single screw extruders, on the other hand, are simpler and less costly, making them suitable for basic applications. The E-GO Series one screw extruders, for example, are customizable in every detail with Digital Extruder Control 4.0, providing precision and efficiency for various plastic extrusion needs, including individual extruders delivering and a single extrusion head.
Co-extrusion Techniques
Co-extrusion is a technique that allows for the combination of multiple materials or colors in a single extrusion, providing both structural and aesthetic benefits. This method enables the fusion and layering of multiple layers to create a composite structure with enhanced properties. For instance, using different materials in co-extrusion can yield products with improved stiffness and resistance to heat.
However, co-extrusion also comes with its challenges. Not all plastics can be co-extruded due to compatibility issues, particularly with polymers that have differing melting points. Despite these challenges, plastic co extrusion remains a valuable technique for producing multilayer films or packaging that enhance product durability and strength.
Quality Assurance in Plastic Extrusion
Quality assurance is paramount in plastic extrusion to ensure that the final products meet desired technical and functional standards. Adhering to industry standards, such as ISO certifications, enhances the reliability and durability of extruded plastic profiles. Bausano, for instance, ensures maximum quality at the technical-functional level during the plastic extrusion process.
These quality control measures contribute to the overall excellence and durability of extruded plastic profiles. Monitoring parameters like temperature, pressure, and speed during the extrusion process ensures consistent product quality and performance.
Choosing the Right Plastic Extruder Manufacturer
Selecting the right plastic extruder manufacturer is crucial for ensuring high-quality production. A strong track record in the plastic extrusion industry is a key indicator of a manufacturer’s reliability. Evaluating the technology and equipment used by a manufacturer can significantly impact production precision and efficiency.
Good communication and after-sales support are essential for building a trustworthy supplier relationship. Customer feedback and references provide valuable insights into a supplier’s reliability and service quality. Additionally, on-time delivery performance is crucial for maintaining production schedules and avoiding disruptions.
Innovations in Plastic Extrusion Technology

The plastic extrusion industry is witnessing significant advancements, particularly with the integration of digital technologies. These innovations allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Energy-efficient designs and advanced heating systems are being developed to reduce energy consumption in plastic extrusion processes, including those involving plastic extruders. The plastics industry is evolving rapidly, adapting to these new technologies.
Incorporating renewable energy sources is another innovative solutions practice being adopted to decrease reliance on fossil fuels. These developments are essential for lowering carbon emissions and promoting sustainability in plastic extrusion manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of plastic extrusion processes is a significant consideration, given the materials used and energy consumed. Key points include:
- Utilizing recycled materials in extrusion processes can significantly reduce environmental impact.
- Co-extrusion techniques can incorporate recycled materials mixed with virgin plastics.
- These methods help reduce material costs and waste.
The plastic extrusion industry is increasingly moving towards a circular economy model by incorporating recycling technologies to minimize the need for new materials. Recent technological advancements, such as induction heating systems and recycling extruders, have enhanced sustainability in plastic extrusion.
Manufacturers are committed to reducing energy consumption and recovering plastic scrap material to lessen their environmental impact.
Summary
In summary, extruded plastic profiles are a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering versatility, efficiency, and customization. The high-volume manufacturing process, coupled with the wide range of materials available, makes plastic extrusion an invaluable technology across numerous industries. From construction to automotive, and medical to packaging, the applications are diverse and impactful.
As we move forward, innovations in plastic extrusion technology and a focus on sustainability will continue to shape the industry. By understanding the intricacies of the extrusion process and the benefits of custom plastic extrusions, manufacturers can leverage this technology to enhance their products and reduce their environmental footprint. The future of plastic extrusion is bright, promising continued advancements and sustainable practices.
]]>Key Takeaways
- Custom extruded plastic profiles are tailored solutions for various industries, including construction, automotive, and healthcare, offering versatility in design and application.
- The extrusion process involves careful material selection, precision shaping, and rigorous quality control to ensure that final products meet specific performance requirements.
- Recent advancements in co-extrusion and secondary operations enhance the functionality and customization of plastic profiles, making them indispensable in modern manufacturing.
Understanding Custom Extruded Plastic Profiles

Custom plastic extrusions are engineered solutions designed to meet specific needs, whether it be unique geometries, complex interactions, or distinctive branding requirements. Unlike stock plastic extrusions, these custom profiles can be tailored to fit exact specifications, making them invaluable in a broad spectrum of applications.
These extruded plastic profiles find their purpose in various sectors:
- In the construction industry, they are used for components like window frames, siding, roofing, and drainage systems.
- In the automotive sector, they serve as trims, seals, and body side moldings.
- In healthcare, they are essential for medical tubing and surgical instruments.
The versatility and adaptability of custom plastic extrusions make them a flexible staple in modern manufacturing.
The Custom Plastic Profile Extrusion Process
The custom plastic profile extrusion process is a marvel of modern engineering, designed for the high-volume production of continuous shapes. This process involves melting plastic and shaping it into profiles that can be either solid or hollow. The precision of custom plastic extrusion allows for intricate designs and tight tolerances, opening up endless design possibilities.
During the extrusion process, in-line operations such as printing and adding tape can be incorporated, enhancing the functionality of the final product. Specialized services like rolling, where plastic film is shaped into tubes, showcase the versatility of this manufacturing processes technique.
Let’s dive deeper into the critical steps of this process, starting with the essential aspect of material selection.
Material Selection for Custom Profiles
Material selection is a pivotal step in the custom plastic extrusion process. The choice of material directly impacts the characteristics of the final product, such as:
- Strength
- Flexibility
- Chemical resistance Selecting thermoplastic materials that align with specific application requirements is essential, including:
- Fire resistance
- Chemical durability
This careful selection process ensures that the custom profiles meet exact specifications and perform well in their intended environments. Selecting the right material enhances the performance and durability of extruded plastic profiles, broadening their suitability for various applications.
Melting and Extruding Plastic Pellets
The journey of custom plastic extrusion continues with the melting and extrusion of plastic pellets. The process involves:
- Feeding plastic pellets into an extruder.
- Plasticizing or melting the pellets due to shear and heat generated by friction.
- Moving the molten plastic through the conveyor.
- Reaching the die, which shapes the molten plastic into the desired profile.
The precision of this process is crucial, as it ensures that the extruded plastic profiles meet the exact specifications required for their intended use. The ability to control the shape, size, and consistency of the profiles during the extrusion process is what makes custom plastic extrusion so versatile and effective.
Shaping and Cutting Extruded Profiles
Once the plastic has been extruded, the process includes:
- Cooling the plastic under water to solidify it before cutting to the desired length.
- Employing advanced techniques to ensure that the profiles are cooled and cut accurately, meeting precise specifications.
- Using operations like thermoforming and ultrasonic welding to further enhance the quality and functionality of the extruded profiles.
The final shaping and cutting processes are integral to producing high-quality custom plastic profiles that fit their intended applications perfectly. Whether it’s a simple tube or a complex, multi-faceted profile, these advanced methods ensure that each piece meets the highest standards of precision and quality.
Benefits of Custom Plastic Extrusions

Custom plastic extrusions offer a multitude of benefits that make them a preferred choice across various industries. One of the most significant advantages is cost-effectiveness:
- High-volume production with custom plastic extrusion is economical due to the continuous operation after die setup.
- It minimizes material waste.
- It reduces overall costs.
This makes it an ideal solution for both custom and large scale production high-volume needs.
Moreover, the material properties of custom plastic extrusions can be tailored to enhance product performance. For instance, adding UV protection or flame retardants can significantly improve the durability and functionality of the final product. Techniques like foamed extrusion create lightweight materials with improved insulation properties, further expanding the applications of custom plastic extrusions.
These benefits, combined with the ability to produce intricate shapes and designs, make custom plastic extrusions a versatile and valuable manufacturing solution.
Innovations in Plastic Co-Extrusion

Plastic co-extrusion is an innovative process that allows for the simultaneous extrusion of multiple materials, resulting in products with enhanced features such as improved barrier properties. Recent advancements in co-extrusion technology and plastic extrusion technologies have enabled manufacturers to produce components with precise control over material layers, enhancing the functionality and performance of custom profiles.
One of the most exciting developments in this field is the integration of 3D printing with co-extrusion, which is revolutionizing prototype development and production capabilities. This combination allows for rapid prototyping and the creation of complex designs that were previously unattainable.
Common applications of plastic co-extrusion include edge trims, seals, and dual-durometer products, which benefit from the enhanced properties provided by co-extrusion technology. Plastic co-extrusion is particularly useful in sectors such as automotive interiors, retail displays, and specialty packaging. By increasing the functionality of custom profiles, co-extrusion offers innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of various industries.
Custom Plastic Tubing Solutions

Customization in plastic tubing allows manufacturers to tailor products to specific design and functional requirements, enhancing their usability. Factors that can be adjusted include:
- Material choice
- Flexibility
- Wall thicknesses
- Specific coatings
This customization ensures that the tubing performs optimally in its intended application.
The performance of plastic tubing can also be adjusted based on its diameter and wall thickness, allowing for tailored applications in various industries. Manufacturers can produce tubing in various shapes, including round and square, to meet specific needs. This flexibility in design and functionality makes custom plastic tubing a versatile solution for many applications.
Industries Utilizing Custom Extruded Plastic Profiles
Custom extruded plastic profiles are essential across a wide range of industries, including:
- Construction sector: used for window frames, siding, and roofing components
- Automotive industry: used for parts like trims, seals, and body side moldings
- Healthcare applications: include medical tubing and surgical instruments, where precision and reliability are paramount
Other industries that utilize custom plastic extrusions include:
- The electrical sector for cable management systems
- Agriculture for irrigation components
- The packaging industry for containers and films
- The marine industry for corrosion-resistant components like boat fenders
- Furniture production for edge banding and shelving systems, along with other components.
The versatility of custom plastic extrusions makes them indispensable in modern manufacturing, especially when considering the benefits of PVC.
Quality Control in Plastic Profile Extrusion
Quality control is a critical aspect of the plastic profile extrusion process. Rigorous testing of raw materials and final products ensures that the extrusions meet the highest standards of integrity and performance. Initial assessments of raw plastic materials focus on verifying their purity and integrity, which is crucial for consistent extrusion results.
Throughout the extrusion process, parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed are continuously monitored to maintain uniform quality. Vacuum calibration is employed to cool and size extruded profiles accurately right after they exit the die.
Final inspections assess properties like color consistency, dimensional stability, and tensile strength, ensuring that the extruded plastic profiles provide adequate structural support and meet the required specifications.
Custom Fabrication and Secondary Operations
Beyond the initial extrusion process, custom plastic profiles often undergo secondary operations to enhance their functionality and usability. These processes can include heat treating, printing, labeling, welding, anodizing, and electroplating. Secondary operations such as notching, drilling, gluing, taping, punching, forming, and heat welding are also available, allowing for further customization.
Selecting a manufacturer that offers these in-house tooling secondary operations can be highly beneficial, as it ensures that the extruded products can be used as-is or fabricated into more complex assemblies that are manufactured. This capability is particularly valuable for projects that require precise customization and assembly, as it streamlines the production process and reduces the need for additional suppliers.
Choosing the Right Custom Plastic Extrusion Manufacturer
Choosing the right custom plastic extrusion manufacturer is crucial to the success of your project. The right manufacturer will:
- Have decades of design, engineering, and manufacturing experience to ensure quality and reliability.
- Possess the capabilities to meet specific application requirements.
- Provide the necessary support throughout the project.
Choosing the wrong manufacturer can lead to product failures, increased costs, and wasted time on rework. Companies like SeaGate Plastics offer cost-effective custom plastic extrusions with quick turnaround times, making them a reliable choice for your extrusion needs.
Ready to Start Your Custom Extrusion Project?
Starting a custom extrusion project is easier than ever. Businesses can upload CAD files to receive instant quotes, ensuring a smooth and efficient start to their projects. Sample parts are provided for approval before full production commences, guaranteeing client satisfaction and alignment with project requirements.
Expert consultation is available to ensure that specifications align with project needs, and services such as custom color matching and packaging design enhance the presentation and marketability of extruded products. Custom plastic extrusion services are offered at competitive prices, especially for high-volume needs.
Summary
Custom extruded plastic profiles offer a versatile and cost-effective solution for a wide range of applications. From the initial material selection to the final product, the extrusion process allows for precise customization and high-volume production. Innovations in co-extrusion and secondary operations further enhance the functionality and usability of these products.
By choosing the right manufacturer and leveraging the benefits of custom plastic extrusions, businesses can achieve their design and functional goals with efficiency and reliability. Whether you’re in construction, automotive, healthcare, or any other industry, custom extruded plastic profiles provide tailored solutions that meet your specific needs.
]]>Key Takeaways
- Key components of a plastic sheet extruder machine include the extruder, die head, cooling rolls, and control system, each essential for high-quality production.
- Types of extruders—single screw and twin screw—offer different advantages, with single screws favored for simplicity and reliability, while twin screws excel in material mixing.
- Choosing the right materials, such as PET, PP, and PC, is vital for the quality and performance of extruded plastic sheets, impacting their applications across industries.
Key Components of a Plastic Sheet Extruder Machine
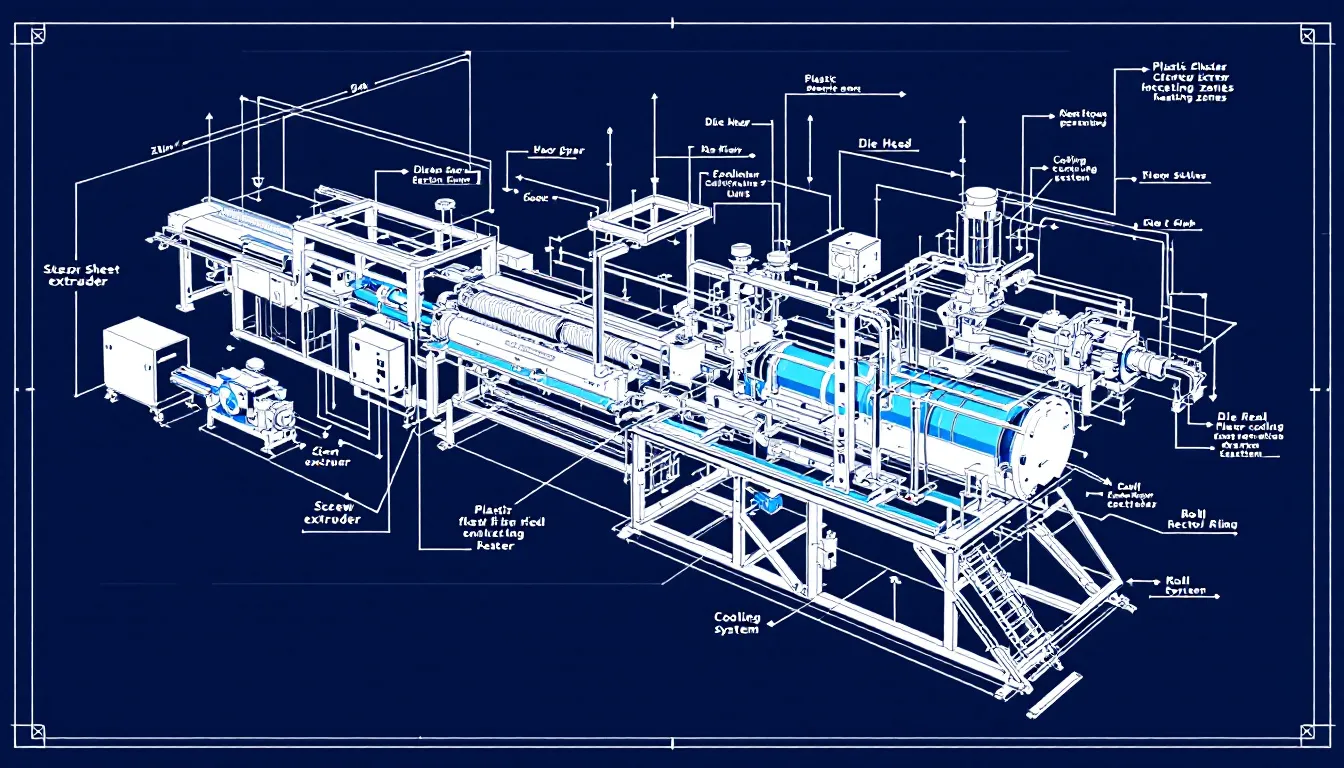
Grasping the key components of a plastic sheet extruder machine is essential for those in the manufacturing process. The main parts include:
- The extruder
- Die head
- Cooling rolls
- The control system Each integral to producing high-quality plastic sheets.
These individual components work in harmony to melt, shape, and solidify plastic materials, ensuring consistency and precision in the final product.
The Extruder
The extruder is the core of the plastic sheet extrusion process, tasked with:
- Melting and homogenizing plastic materials.
- Utilizing rotating screws to blend the plastic uniformly, ensuring a consistent flow of molten plastic.
- Mixing and transporting the material.
- Generating the needed heat for melting.
Whether using single or twin screws, the efficiency and reliability of several extruders are critical for producing high-quality plastic sheets.
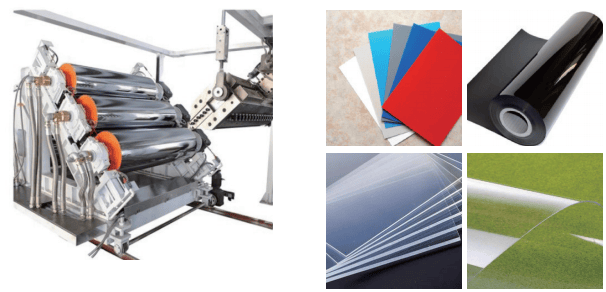
Die Head
The die head is where the magic happens, shaping the molten plastic into sheets with precise thickness. In sheet extrusion, T-shaped, coat-hanger dies, and flat dies are commonly used to achieve the necessary sheet profiles. However, improper die design can lead to clogging issues, impacting the final product’s quality.
Therefore, meticulous attention to die head design is crucial for optimal performance.
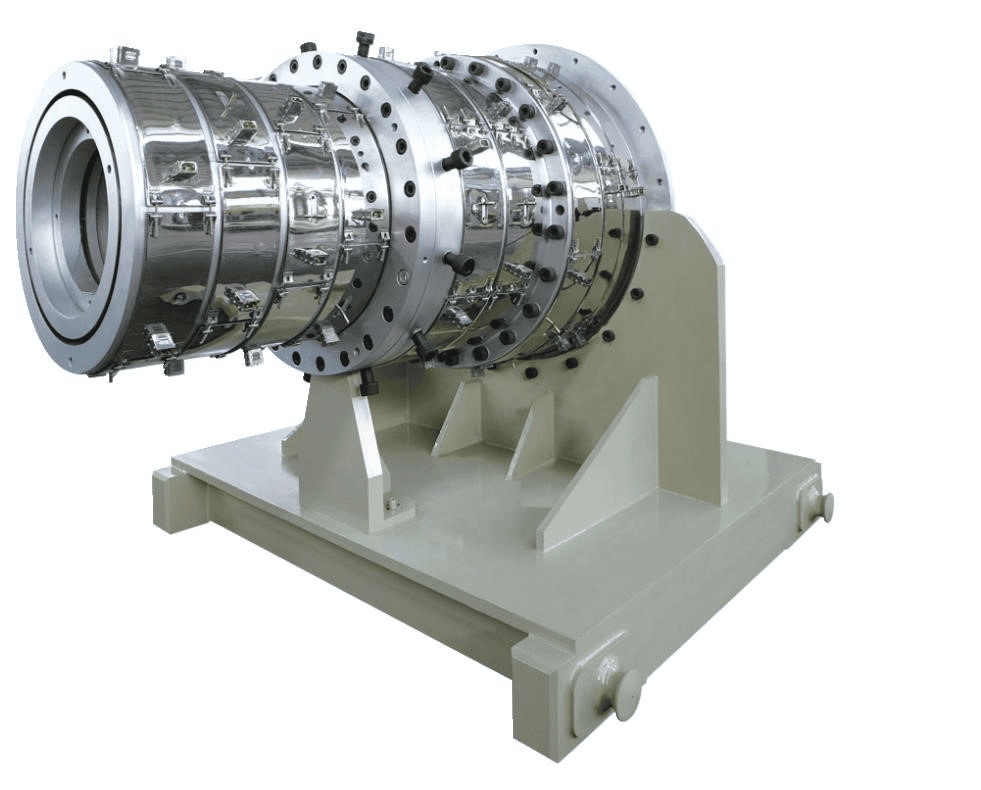
Cooling Rolls
Cooling rolls are critical in the plastic sheet extrusion process, playing a vital role in solidifying the extruded material. They maintain a uniform temperature, ensuring that the plastic sheets cool evenly and retain their intended shape and properties.
Effective temperature control via cooling rolls is vital for producing high-quality plastic sheets.
Control System
The control system is the brain of the plastic sheet extruder machine, managing critical parameters such as temperature and speed. Precise management of these parameters ensures the consistent quality of the extruded sheets.
Maintaining optimal conditions throughout the extrusion process, the control system is pivotal in achieving high production efficiency and product quality.
Types of Plastic Sheet Extruder Machines
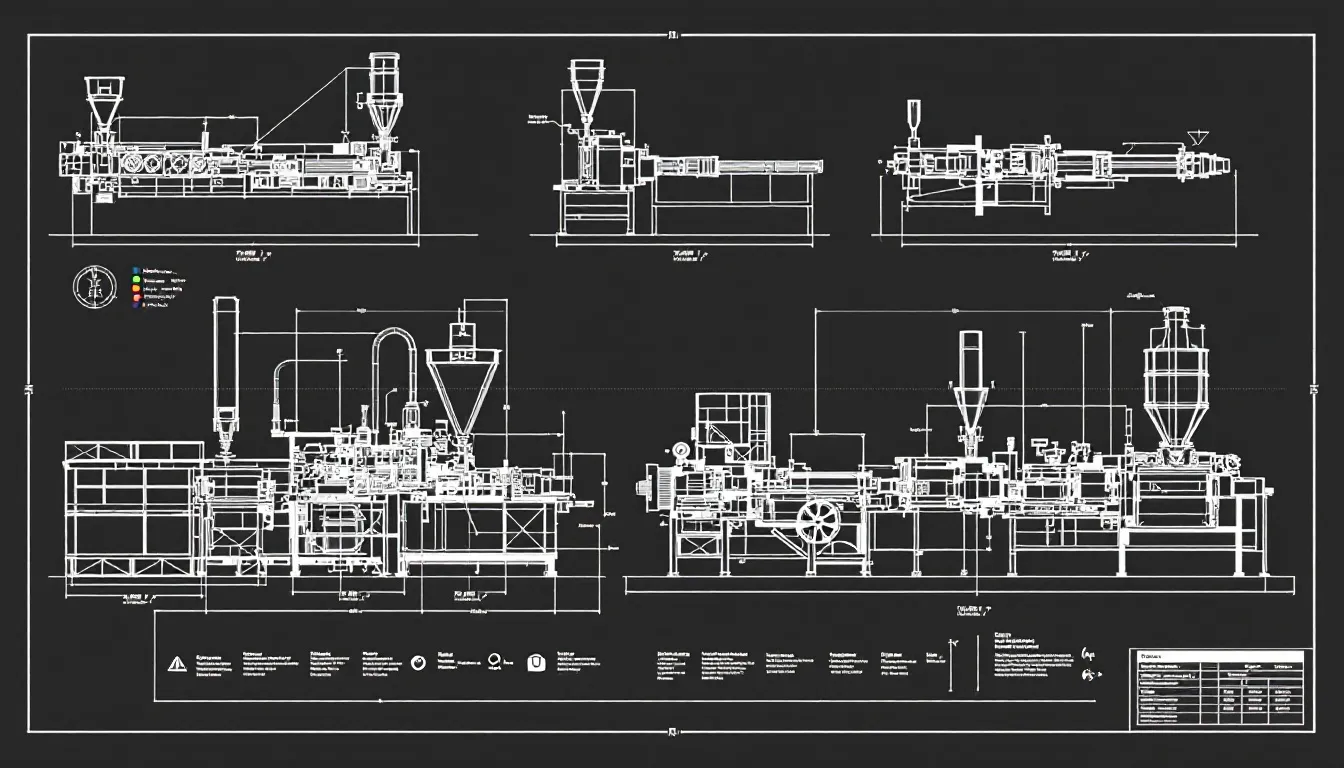
Plastic sheet extruder machines come in various types, with single screw and twin screw extruders being the most common. Each type has its unique advantages and is suited for different applications. Recognizing these differences helps in selecting the right machine for your specific needs, be it simplicity and ease of operation or advanced mixing capabilities.
Single Screw Extrusion Machines
Single screw extrusion machines are renowned for their simplicity and reliability. They are widely used in plastic sheet production due to their straightforward one screw operating and maintenance.
Industries ranging from food packaging to automotive benefit from the versatility of these machines, making them a staple in many manufacturing processes. Their design allows for efficient processing of various plastic materials, ensuring consistent product quality.
Twin Screw Extrusion Machines
Twin screw extrusion machines offer superior mixing capabilities, making them ideal for processing complex materials. They come in two sub-types: co-rotating and counter-rotating, each with specific advantages.
While co-rotating extruders provide excellent ingredient uniformity, counter-rotating extruders can handle higher pressure build-up, enhancing operational efficiency. These machines are essential for applications requiring precise material blending and high-quality outputs through coextrusion.
Materials Used in Plastic Sheet Extrusion
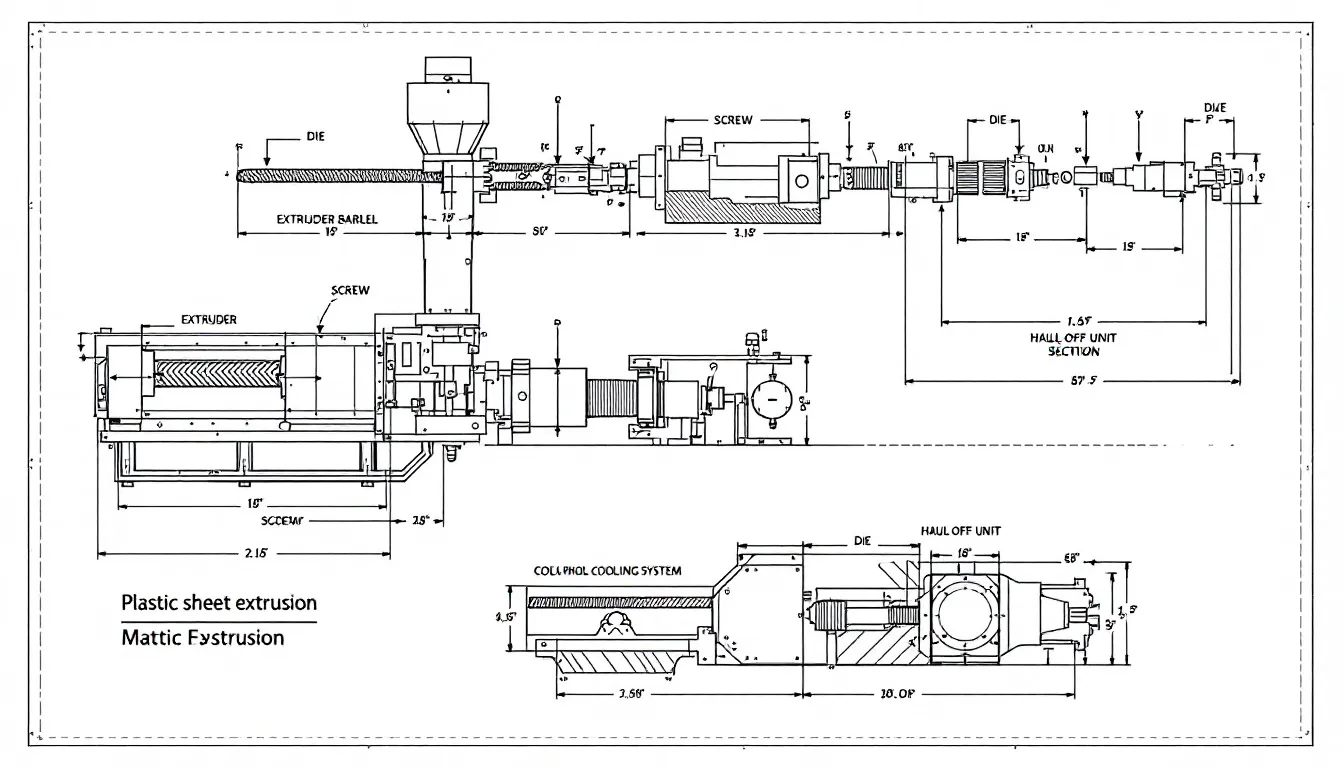
Choosing the right materials for plastic sheet extrusion is critical for achieving the desired properties in the final product. Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polycarbonate (PC), each offering unique benefits.
The choice of material impacts not only the extrusion process but also the performance and durability of the plastic sheets.
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) is a thermoplastic polymer widely used in plastic sheet production due to its excellent strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. Its versatility makes it a preferred choice for various applications, including packaging, automotive components, and medical devices.
PET’s performance in extrusion processes highlights its essential role in manufacturing high-quality plastic sheets.

Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene (PP) is a highly versatile material used in numerous industrial applications. Its strength increases with higher ethylene content in its copolymer forms, making it ideal for automotive and industrial sectors.
PP’s robustness and resistance to chemicals and moisture make it a valuable material in plastic sheet extrusion.

Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate (PC) is renowned for its impact resistance, making it suitable for protective barriers and high-stress applications. Industries benefit from PC’s ability to produce high-quality sheets that can withstand significant physical stress, ensuring durability and reliability in various industrial applications.

The Plastic Sheet Extrusion Process
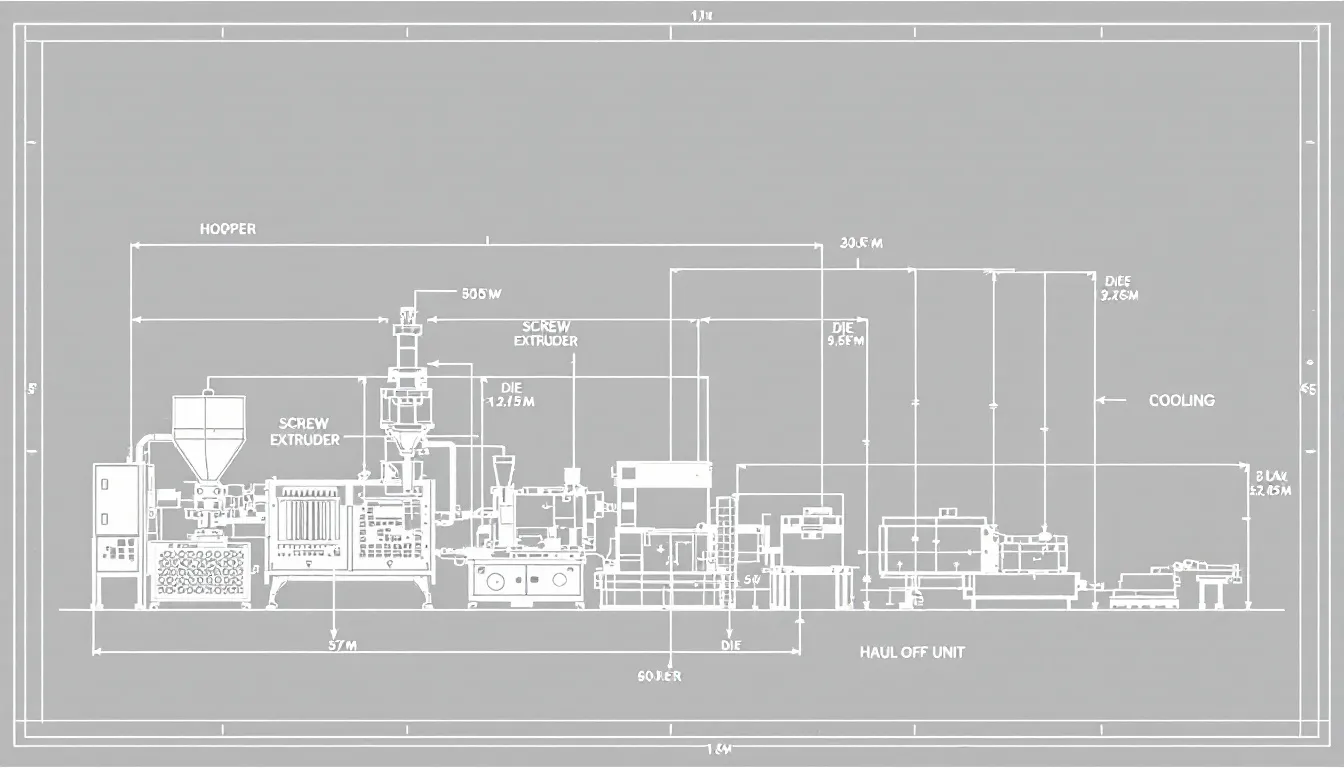
The plastic sheet extrusion process is a meticulous sequence of steps that transform raw materials into high-quality processed plastic sheets, with further processing involved. It begins with feeding raw materials into the extruder, followed by melting and mixing, and culminates in shaping and cooling the molten plastic using plastic sheet extrusion lines.
Each step is critical for ensuring the consistency and quality of the final product.
Feeding Raw Materials
The journey of plastic sheet extrusion begins with the introduction of raw materials. These materials:
- They are usually in pellet or plastic granule form
- Are fed into the extruder
- They are introduced through a hopper
- They are transported to the feed zone, where they begin to melt and mix.
Proper feeding is essential for maintaining a consistent flow and quality of the final product.
Melting and Mixing
Once in the extruder, the raw materials are gradually melted and homogenized using a rotating screw in a heated cylinder. The mechanical energy generated by the screws helps achieve the desired consistency and flow characteristics of the molten plastic.
Maintaining optimal thermal properties and temperature control is critical for ensuring a smooth and efficient extrusion process.
Shaping and Cooling
The molten plastic is then forced through a die, shaping it into continuous sheets. Cooling rolls rapidly cooled the shaped material, solidifying it into the desired form through injection molding.
Effective temperature control during this phase is essential for preventing warping and ensuring uniform thickness and texture in the final product.
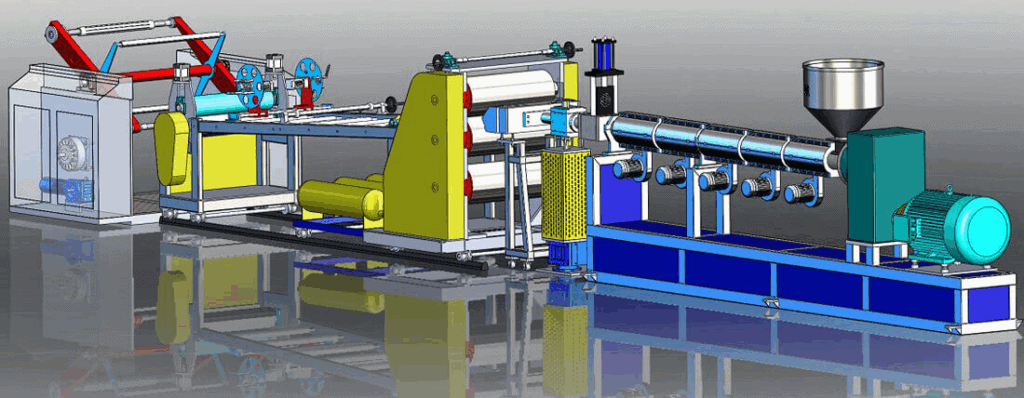
Optimizing Plastic Sheet Extrusion
Optimizing the plastic sheet extrusion process is key to enhancing production efficiency and product quality. Manufacturers can employ various strategies, including:
- Equipment adjustments
- Process parameter tuning
- Material selection improvements. These optimizations ensure consistent product quality and reduce operational costs.
Equipment Adjustments
Regular maintenance and adjustments of plastic sheet extruder machines are key to optimal performance. Scheduled checks help identify potential issues before they escalate, ensuring longevity and consistent operation.
Adjusting machine settings, such as screw configurations and temperature controls, can significantly improve throughput and product quality.
Process Parameter Tuning
Fine-tuning process parameters like temperature and screw speed is crucial for optimizing the efficiency and quality of plastic sheet extrusion. Advanced technologies and detailed analyses can identify inefficiencies and opportunities for enhancement, leading to better product consistency and overall process efficiency.
Material Selection Improvements
Selecting the right plastic materials is fundamental to improving the extrusion process and the final product’s performance. Proper plastic material selection minimizes issues related to inconsistent raw materials, ensuring high-quality outputs.
Commonly used materials like PET, PP, and PC offer specific properties that enhance the extrusion process and meet various application needs.
Common Challenges in Plastic Sheet Extrusion
Plastic sheet extrusion is not without its challenges. Issues such as temperature control, screw speed, air pressure adjustments, and pressure adjustments can affect the quality and consistency of the final product.
Addressing these challenges through effective management and optimization strategies is key to producing high-quality plastic sheets.
Material Inconsistencies
Inconsistent raw materials can lead to significant product defects, including surface imperfections and improper thickness. Implementing strict quality control measures and sourcing materials from reputable suppliers can help manage these inconsistencies.
Advanced blending techniques also help ensure consistent product quality.
Die Clogging
Die clogging is a common issue that can disrupt the flow during the extrusion process, leading to uneven thickness or defects in the final product. Using appropriate filters and maintaining the die head can help mitigate this problem, ensuring a smooth and consistent extrusion process.
Cooling Issues
Effective cooling is crucial for preventing defects like warping and maintaining the quality of extruded plastic sheets. Proper temperature control and cooling management ensure uniform thickness and texture, resulting in high-quality final products.
Manufacturers must prioritize cooling systems to achieve consistent and reliable outputs.
Applications of Plastic Sheets
Plastic sheets are integral to a wide range of industries, from automotive to food packaging and medical devices. Their versatility and adaptability make them essential in manufacturing processes, providing solutions that meet specific industry requirements.
The following subsections explore some of the key applications of plastic sheets.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, plastic sheets are widely used to manufacture various automotive parts and components. Extruded sheets are specifically utilized for dashboards, protective panels, and other interior elements.
Polypropylene, in particular, is highly valued for its strength and durability, making it an ideal choice for vehicle interiors and other high-stress applications.
Food Packaging
Plastic sheets, especially those made from PET, play a crucial role in food packaging, providing durable and safe solutions for storing and transporting food products. These plastic sheets can be produced from both virgin and recycled materials, enhancing their sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
Their clarity and strength make them ideal for forming trays, lids, and flexible packaging.

Medical Devices
The use of plastic sheets in medical devices is essential for ensuring product sterility and safety. These sheets are designed to withstand chemical exposure and are easy to clean, making them suitable for a variety of medical applications.
Their role in the production of medical devices highlights their importance in maintaining high standards of hygiene and effectiveness.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Plastic Sheet Extruder Machine
Selecting the right plastic sheet extruder machine is crucial for optimizing production efficiency and product quality. Key factors to consider include the manufacturer’s reputation, customization options, and energy consumption.
These considerations ensure that the chosen machine meets specific production requirements and supports sustainable manufacturing practices.
Manufacturer Reputation
Choosing a reputable manufacturer is critical for ensuring the reliability and performance of plastic extrusion machines. Evaluating customer feedback and case studies can provide insights into a manufacturer’s service quality and reliability.
Well-regarded brands like Davis-Standard are known for their high-quality equipment and exceptional support, making them a preferred choice in the industry.

Customization Options
Customization options are essential for meeting specific production requirements in plastic sheet extrusion. Features such as adjustable sheet thickness, texture, and color allow manufacturers to produce sheets tailored to their needs.
Companies like Bixby International and Reifenhäuser Group offer customized sheet production lines, ensuring versatility and adaptability in various applications.
Energy Consumption
Energy efficiency is a critical factor in plastic sheet extrusion, influencing operational costs and environmental sustainability. Energy-efficient machines reduce the carbon footprint and promote greener production practices.
By choosing energy-efficient equipment, manufacturers can lower operational costs and contribute to sustainable manufacturing.
Summary
Plastic sheet extruder machines are indispensable in the manufacturing industry, offering versatility and efficiency across various applications. Understanding the key components, types, and materials used in these machines is essential for optimizing production processes and ensuring high-quality outputs. From feeding raw materials to shaping and cooling, each step in the extrusion process plays a crucial role in determining the final product’s quality and consistency.
Addressing common challenges and optimizing the extrusion process through equipment adjustments, process parameter tuning, and material selection improvements can significantly enhance production efficiency. When choosing a plastic sheet extruder machine, factors such as manufacturer reputation, customization options, and energy consumption should be carefully considered to meet specific production needs and support sustainable practices. By staying informed and making strategic decisions, manufacturers can achieve consistent product quality and operational excellence.
]]>
Introduction to Plastic Recycling
- Plastic recycling is a crucial process that helps reduce plastic waste and conserve resources by transforming waste plastics into valuable materials.
- The plastics recycling industry has grown significantly, with various technologies and machines being developed to improve recycling efficiency and quality.
- Recycling plastic packaging, such as plastic containers and bottles, is essential to reduce plastic pollution and promote a circular economy.
- Plastic recycling machines, including plastic recycling extruders, play a vital role in processing waste plastics into high-quality products.
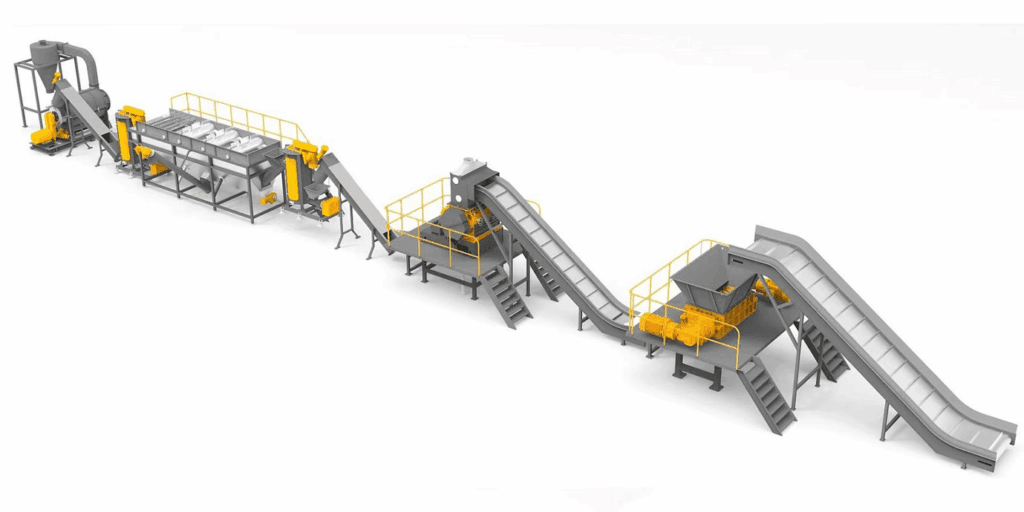

The Recycling Process
- The recycling process involves collecting and sorting recyclable materials, including plastic items, and processing them into raw materials.
- Material recovery facilities (MRFs) use conveyor belts and other equipment to sort and separate plastics from other materials.
- The sorted plastics are then washed and processed into different types of plastic, such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE).
- Recycling facilities use various machines, including plastic recycling extruders, to produce high-quality recycled plastic products.
Types of Plastics
- There are several types of plastics, including PET, HDPE, PVC, and others, each with its own unique properties and recycling challenges.
- Some plastics, such as PET and HDPE, are commonly recycled and used to produce new products, such as bottles and containers.
- Other plastics, such as PVC, are rarely recycled due to the lack of efficient recycling technologies and high processing costs.
- Understanding the different types of plastics and their recycling processes is essential to develop effective recycling strategies.
Plastics Recycling Technologies
- Various plastics recycling technologies are available, including mechanical recycling, chemical recycling, and other processes.
- Mechanical recycling involves melting and reforming plastics into new products, while chemical recycling breaks down plastics into their raw materials.
- Advanced recycling technologies, such as plastic recycling extruders, can produce high-quality recycled plastics with minimal contamination.
- The choice of recycling technology depends on the type of plastic, the desired product quality, and the available equipment and resources.
Applications of Plastic Recycling Extruders
- Plastic recycling extruders are commonly used to produce high-quality recycled plastics for various applications, including packaging materials, containers, and other products.
- These machines can process different types of plastics, including PET, HDPE, and PVC, and produce a wide range of products, from plastic bags to plastic lumber.
- Plastic recycling extruders are also used to produce recycled plastics for use in construction, automotive, and other industries.
- The use of plastic recycling extruders can help reduce plastic waste, conserve resources, and promote a circular economy.

Benefits of Plastic Recycling
- Plastic recycling offers several benefits, including reducing plastic waste, conserving resources, and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Recycling plastic packaging, such as plastic bottles and containers, can help reduce plastic pollution and promote a sustainable environment.
- The use of recycled plastics can also reduce the demand for virgin plastic, decrease energy consumption, and lower production costs.
- Additionally, plastic recycling can create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and contribute to a more circular economy.

Conclusion
- In conclusion, plastic recycling is a vital process that can help reduce plastic waste, conserve resources, and promote a circular economy.
- The use of plastic recycling extruders and other recycling machines can produce high-quality recycled plastics for various applications.
- By understanding the different types of plastics, recycling technologies, and applications of plastic recycling extruders, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions about plastic recycling and contribute to a more sustainable environment.
- Ultimately, plastic recycling requires a collective effort from governments, industries, and individuals to reduce plastic waste, promote recycling, and create a more sustainable future.

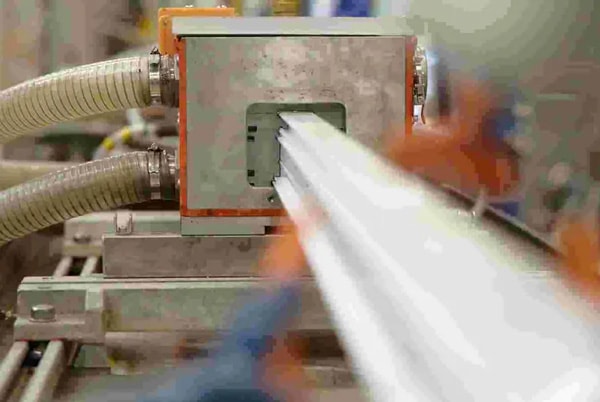
1) What is the Reason Behind China’s Popularity for Plastic Extruders?
China’s plastic extruder manufacturing industries provide rapid refinement of machinery while keeping costs low. Whether launching a new product or scaling business operations, China’s extrusions provide unmatched performance and value.
- Advanced Manufacturing at Lower Costs
China’s plastic industry factories offer powerful machines and equipment at a lower cost compared to the US and Europe. Their use of sophisticated supply chains and mass production makes them offer unrivalled value for their equipment.
- Innovation Backed by R&D
Leadership in various machinery co ltd sectors improves the China plastic extruder design, like screw design, smart controls, and heater efficiency. It is all done by working with universities, funded research labs, and tech.
- Scope and Flexibility
China has it all, from lab scale to industrial extruders, even to sheets, pipes, and films, including biodegradable options. Moreover, machines can be tailored for your specific application, from screw diameter to output rate and even system size.
- Reputation and Readiness for Exports
Ensured quality providers have CE, UL, and ISO compliance. Another good thing is that reliable suppliers are familiar with shipping, handling, and serving documentation and certification demands for international clientele.
- Immediate Client Servicing and shipping
Staff who speak English, combined with virtual site visits and expedited shipping, mean timely servicing and seamless interaction. Contact and parts are delivered and replenished in days.
- Case In Point
- A Brazilian company implemented a Chinese PET sheet production line for food packaging in 27 days.
- An Indian company that had just started took on a Chinese PLA film extruder to produce compostable bags.
2) Kinds of Plastic Extruders You Can Source from China
China’s extrusion plastic industry has a wealth of machines to meet various types of production requirements. Single screw extruders, custom single screw extruders, and twin screw extruders are the most common ones. Here’s a comparison between the two.

i) Twin Screw Extruders
Complex tasks requiring extensive processing, as well as output and blending of the material, are best served with twin screw extruders. Chinese manufacturers have refined these machines to handle applications such as:
- Plastic granulation with additives or color masterbatch
- Producing multi-layered films and sheets
- Pipe and profile extrusion
- Biodegradable and other specialty blends
- Why choose them?
Their performance in mixing and blending various materials is unmatched ,along with high melt quality. Chinese twin-screw extruders with a torque rating of 14 Nm/cm³ and speeds of 1800 RPM offer unrivalled performance.
ii) Custom Single Screw Extruders
Single screw extruders are less complicated and more suited for simpler projects with minimal mixing requirements. Chinese suppliers offer custom designs tailored to your desired material, output, and budget. Their applications include:
- Cable sheathing
- Small-diameter tubing
- Basic profiles and 3D printing filament
- Why choose them?
They are more affordable, have low operational and maintenance demands, and are best for low to mid-volume production.
Which Should You Choose?
- Opt for twin screw extruders if you’re dealing with multi-component materials or require high throughput.
- A single screw is ideal if your focus is on simple thermoplastics and if you prefer less complexity during setup.
You can fully customise your machine on whichever model you prefer with China’s vast sourcing capabilities.
3) Specialized Plastic Extrusion Lines
China is not just a supplier for general-purpose extruders, but is also a provider for industry-specific turnkey project extrusion lines designed with precision for performance, quality, and speed. Here are some solutions from top Chinese sellers:

a) PPR Pipe Production
These machines manufacture 3-layer PPR pipes with a fibreglass middle layer that enhances the strength and thermal resistance of the pipes. Their dust-free cutting systems provide seamless edges that minimise the need for post-processing, making them ideal for plumbing and heating systems.
b) Dip Tube Manufacturing
Dip tubes are used in spray and pump bottles. Chinese dip tube extruders work with thermoplastic elastomers and feature angle cuts to avoid leakage and blockage.
c) PVC Braided Hose Lines
These PVC extruder lines possess high tenacity polyester yarn-embedded inner and outer PVC layers. This results in a flexible and strong hose used in construction and appliances, and in gardening. Bonding excels in enhancing integrity and clarity.
d) Multi-Color Shower Hose Extrusion
These lines produce multi-colour glossy shower hoses for sanitary products employing heat-transfer coating and EU-compliant colour sheets for an appealing and safe finish.
e) PC/PMMA Profiles for LED Covers
These extruders develop optical-grade LED profiles for lighting. Co-extrusion latest technology, permits amalgamating PC and PMMA for UV resistance, clarity, and structural integrity.
f) TPE Elastic Strip Extrusion
These lines produce strips used in packaging, seals, and wearable technology. Thicker uniform strips are achieved with calibrated cooling rollers, tight thickness control, and flexibility.
Most of these extrusion lines are modular units and turnkey systems, designed to fit the client’s requirements.
4) Advancements in Technology and Smart Control
With the aid of global supply chains and innovation programs, China’s plastic extrusion machine industry is successfully competing with European companies in several critical areas due to its extensive experience. Now, Chinese manufacturers can produce extruders that are on par with European systems.
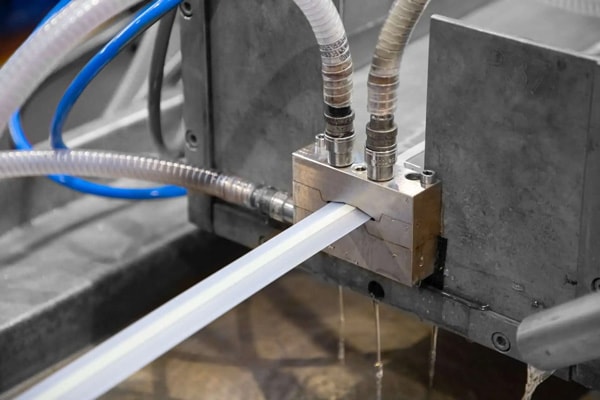

Modular Configuration of Chinese Extruders
Today’s Chinese extruding machinery co ltd is modular, enabling the users to select feeder systems and die heads, screws, and barrels of varying lengths. This drastically lowers the chances of underperformance during production and expediting development time.
In addition, many of the essential parts, which are important for reliability, such as control systems, motors, and even gearboxes, are integrated from top international manufacturers.
Smart Control Systems
No doubt, the evolution of artificial intelligence is occurring at a rapid pace. A number of Chinese equipment now includes smart features such as real-time fault monitoring, automated process supervision, and smart temperature regulators. These functions enhance stability, lessen manual mistakes, and minimise waste. Even some systems are capable of cloud-based remote diagnostics, too.
Alright, China now serves as more than just a cost-effective manufacturing option, as the country has become an innovation centre. Chinese extruders are positioned as forward-looking options for manufacturers who need smart technology, adaptability, and operational performance.
5) How Faygoplas Supports Your Plastic Extrusion Projects
It is essential to assess your design, material, and process validation before you are fully committed to a complete extrusion line. This is where Faygoplas can strategically help you. We are among the foremost rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing firms established in China, with extensive experience.
We help as a backbone in the transition from concept to production, which helps manufacturers scale up with certainty.
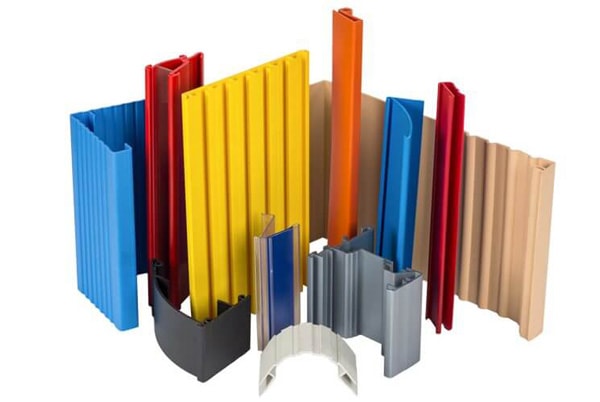

- Rapid Prototyping for Dies and Parts
Faygoplas helps in testing new extrusion shapes and custom profiles with remarkable precision to prototype the dies with the aid of CNC machining and 3D printing for nozzles, fittings, and end-use components. This helps you assess how the plastic will act in real-world plastic extrusion scenarios prior to any tooling expenditure.
- Design and short-run Faygoplas feedback sessions
At Faygoplas, we always make an effort to delve deeper than simply building what you send us. Well, every submission undergoes CAD file inspection to uncover potential weak points, material flow issues, and overall, any concerning tolerances.
To make it better, you get feedback and suggestions from seasoned engineers experienced with various industries and extrusion setups, allowing you to sidestep costly blunders.
- Short-run Production for Feasibility Testing
Do you need to test a product for market acceptance, product durability, or any other test? At Faygoplas, our mission includes conducting small batch productions that allow you to test products along their full life cycles. You can also replicate extrusion behaviour to work on packaging, fit, or function without running an entire production line.
- Minimising Investment Risk, Faygoplas Approach
With us, there’s no lasting investment to be made in custom extruders or permanent molds. We take an iterative method by allowing you to refine, improve, and test your extrusion concept. This is a great option for startups, R and D departments, along any product teams looking to test new formulations or designs.
- Real Customer Experiences
Good to share that clients who worked with professional Chinese plastic Extruder firms have cited the use of their machines for decades, along with their customer service. Clients emphasised that the high service responsiveness, low downtimes, and stable output quality all contributed to the enduring use of the machines.
Others praise the speed of contact response and replacement part sales. Faygoplas’s employees are often credited for offering feedback that reduced errors in early-stage granulation and product validation.
Conclusion
China, in particular, the Jiangsu province and Zhejiang provinces, is the largest producer of plastic extruders in the world. Their manufacturers are well-equipped, with industry-competitive pricing, and leverage modern technology.
With trusted suppliers and industry leaders like Faygoplas, China’s plastic industry advantages are ready to be explored, assuring that you’re supported throughout the manufacturing process. You can contact us right now!
]]>- Plastic extruders are essential machines in manufacturing, transforming raw plastic materials into a variety of products through a three-zone process: feed, melting, and metering.
- Various types of plastic extruders, including single screw and twin screw, belong to distinct categories tailored to specific processing needs, affecting the efficiency and quality of the extrusion process.
- Regular maintenance, including cleaning and component inspection, is crucial for the operational efficiency and longevity of plastic extruders, ensuring consistent production quality.
Understanding Plastic Extruders
Plastic extruders are indispensable machines in the manufacturing industry, vital for shaping and processing plastic materials into numerous products. This technology is widely used in the plastics industry, producing high-quality products with uniform properties using an extruder machine, an extrusion machine, a plastic extrusion machine, plastic extrusion machinery, and plastic extrusion equipment. Plastic extrusion plays a crucial role in this process.
Everyday products, from simple plastic containers to complex automotive industry parts, owe their existence to this sophisticated equipment machine machines.
How Plastic Extruders Work
The magic of plastic extruders lies in their ability to transform raw plastic materials into finished products through a process of melting, processing, and re-melting plastic polymers. This intricate process is broken down into three critical zones: the feed zone, the melting zone, and the metering zone.
Each zone is vital for the proper processing and shaping of the plastic material into the desired form.
The Feed Zone
In the feed zone, the journey of plastic resins begins. These resins, typically in pellet form as small pellets or beads, are introduced into the extruder. The material can enter the extruder either by gravity fed in a process known as flood feeding or at a controlled rate called starve feeding.
The hopper, designed to ensure a consistent flow of materials, plays a critical role here. Temperature control is essential in this zone to ensure the plastic starts adhering to the barrel, although it remains in a solid state at this stage.
The Melting Zone
As the plastic moves from the feed zone, it enters the melting zone where the real transformation begins. Here, the plastic material is subjected to heat generated from the turning screws and heating components of the extruder.
The plastic gradually melted, transitioning from a solid to a molten state, ensuring a consistent melt. This phase prepares the material for its final shaping.
The Metering Zone
In the metering zone, the molten plastic is readied for its final form. This zone is crucial for preparing the plastic to be forced into a die, where it will be shaped into the desired product.
The metering zone ensures uniform temperature melting and maintains consistent air pressure and flow toward the die, crucial for achieving a high pressure, high-quality final product.
Types of Plastic Extruders
Plastic extruders come in various types, each suited for different materials and applications. The primary categories are single screw, twin screw, and ram extruders. The choice of extruder impacts the efficiency and quality of the extrusion process, depending on the specific requirements of the plastic material.
Single Screw Extruders
Single screw extruders are the most common type found in the industry, known for their straightforward design and reliability. They are particularly effective for producing continuous lengths of plastic products, such as pipes and tubing.
Different plastics require specific temperature settings and processing conditions, making the right extruder selection vital for optimal performance.
Twin Screw Extruders
Twin screw extruders, available in co-rotating and counter-rotating types, offer higher axial velocity and better mixing capabilities compared to single screw extruders. This makes them ideal for processing complex plastic materials that require precise mixing and melting conditions using twin screw extrusion machines.
Choosing between co-rotating and counter-rotating depends on the specific properties of the plastic being processed.
Applications of Plastic Extruders
Plastic extruders are versatile machines used across various industries, including construction, automotive, and packaging. The extrusion process transforms thermoplastic materials into continuous products like pipes, films, and medical supplies by melting and shaping them through a die. This process is economical and allows for creating products in various colors, shapes, and finishes.
Pipe and Tubing Extrusion
Pipe and tubing extrusion is a significant application of plastic extruders. Machines designed for this purpose can produce PVC pipes with diameters ranging from 16-1000mm for use in agriculture and construction. HDPE pipe extrusion machines are particularly suited for industrial piping systems, such as underground gas and water pipelines.
These machines’ ability to produce tube pipes of any length and integrate components like couplers with rubber seals during the extrusion process adds to their versatility.
Sheet and Film Extrusion
Plastic extruders are also extensively used in the production of plastic sheets and films. The dies in sheet and film extrusion allow for the continuous extrusion of polymer melt, which can then be used for glazing doors, windows, or as protective plastic sheet against environmental factors.
Blown film extrusion, a subset of this application, produces items such as food packages and shopping bags.
Profile Extrusion
Profile extrusion involves creating custom plastic profiles that meet diverse production needs. This application is crucial across various industries, enabling the production of unique shapes and sizes tailored to specific requirements.
Profile extrusion offers significant flexibility and precision, whether for automotive parts or decorative panels.
Key Components of a Plastic Extruder
A plastic extruder consists of several key components, each playing a vital role in the extrusion process. The main parts include the feed hopper, barrel, screws, die, and cooling system.
Understanding these components and their functions is crucial for anyone involved in operating or maintaining plastic extruders.
The Hopper
The hopper, the starting point of the extrusion process, introduces raw plastic materials into the extruder in various forms:
- Pellets
- Granules
- Flakes
- Powders It ensures a consistent feed of materials, which is crucial for maintaining the quality and efficiency of the extrusion process.
The Barrel and Screws
The barrel and screws are central to the extruder’s screw operating. The barrel provides the necessary heat and pressure to melt the plastic, while one screw conveys, mixes, and homogenizes the material as it moves towards the die.
This ensures that the plastic is uniformly melted and ready for shaping.
The Die
The die is a critical component that shapes the molten plastic into the final product. It is engineered to create specific shapes and profiles, allowing for a wide range of sizes and designs.
The precision of the die determines the quality and consistency of the extruded product.
Benefits of Using Plastic Extruders
Plastic extruders offer numerous benefits, making them a preferred choice in various manufacturing processes. They provide cost advantages, enable high-volume production, and allow for significant customization.
Additionally, modern extruders are designed with sustainability in mind, reducing energy consumption and facilitating recycling.
High Volume Manufacturing
A major benefit of plastic extruders is their ability to support a high volume manufacturing process. The extrusion process is highly efficient, enabling large-scale production of continuous products. This makes it ideal for industries that require mass production, such as automotive and construction.
Customization and Flexibility
Plastic extruders offer unparalleled customization and flexibility. They can be easily adjusted to accommodate different materials and specifications, allowing manufacturers to create unique shapes and sizes.
This flexibility is crucial for meeting specific project requirements and ensuring high-quality products.
Sustainability and Recycling
Sustainability is a significant consideration in modern manufacturing, and plastic extruders are no exception. They help reduce environmental impact by enabling the efficient use of recycled materials and minimizing waste.
Companies like Bausano are at the forefront of offering solutions that reduce energy consumption and enhance the recovery of plastic scrap.
Choosing the Right Plastic Extruder

Selecting the right plastic extruder involves considering several factors:
- Material compatibility
- Output requirements
- Additional features
- Customization options
- Cost factors These all play a crucial role in making the right choice.
This section provides guidance on how to navigate these considerations to find the best extruder for your needs.
Material Compatibility
Material compatibility is paramount when choosing a plastic extruder. The extruder must be able to process the specific plastic material efficiently to ensure high-quality output.
Different thermoplastic materials offer versatility in manufacturing, making it essential to match the extruder with the right material.
Output Requirements
Understanding the output requirements is crucial for selecting an appropriate extruder. The capacity to meet production demands while maintaining efficiency and cost-effectiveness is a key consideration.
Matching the extruder’s output capacity with the type of plastic material ensures optimal performance and quality.
Additional Features
Additional features such as advanced cooling systems, automatic temperature controls, and specialized screws can significantly enhance the performance of plastic extruders.
These optional accessories and enhancements improve the overall efficiency and quality of the extrusion process.
Maintenance and Care of Plastic Extruders
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term operation and efficiency of plastic extruders. It helps prevent contamination, identify wear and tear early, and address complex issues through professional servicing.
Proper maintenance practices enhance the lifespan and productivity of extruders.
Regular Cleaning
Keeping the extruder clean is crucial for preventing contamination that can lead to defects in the final product. Regular cleaning prevents the buildup of material residues, maintaining consistent production quality.
Component Inspection
Routine inspection of key components helps prevent serious failures by identifying early signs of wear. Key points include:
- Inspecting screws and barrels regularly
- Spotting potential issues before they escalate
- Ensuring the extruder operates efficiently
- Reducing downtime
Professional Servicing
Professional maintenance ensures accurate diagnosis and effective resolution of complex issues. This professional servicing can address intricate technical problems that regular maintenance might overlook, enhancing the overall performance of the extruder.
Summary
Plastic extruders are indispensable in modern manufacturing, playing a critical role in producing a wide range of plastic products. Understanding how they work, the different types available, their applications, and the benefits they offer is essential for optimizing their use. Regular maintenance and careful selection of the right extruder can significantly enhance production efficiency and product quality. Embrace the potential of plastic extrusion to innovate and elevate your manufacturing processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of plastic extruders?
The main types of plastic extruders are single screw extruders, twin screw extruders, and ram extruders, each designed for specific materials and applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the right extruder for your needs.
How does the feed zone in a plastic extruder work?
The feed zone in a plastic extruder facilitates the introduction of pelletized plastic resins, which are gradually heated and begin to adhere to the barrel, ensuring a consistent flow into the melting zone. This initial stage is crucial for effective processing of the material.
What is the role of the die in a plastic extruder?
The die in a plastic extruder plays a crucial role by shaping the molten plastic into the desired final product, thereby determining its size and profile as it exits the machine. This precision is essential for achieving the intended specifications of the extruded material.
Why is regular maintenance important for plastic extruders?
Regular maintenance is crucial for plastic extruders as it prevents contamination, detects wear and tear early, and optimizes operational efficiency, ultimately extending the equipment’s lifespan and ensuring high product quality.
How do plastic extruders contribute to sustainability?
Plastic extruders significantly enhance sustainability by efficiently utilizing recycled materials, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing waste in the manufacturing process. This leads to more environmentally responsible production methods.
]]>- Recycling extruders convert plastic waste into reusable materials, enhancing sustainability and the quality of recycled products through controlled melting processes.
- Single screw and twin screw extruders serve distinct roles in recycling, with twin screw extruders offering greater versatility in handling various contaminated plastics.
- Modern recycling extruders are designed with advanced features that improve efficiency, product quality, and cost-effectiveness, making them essential for effective plastic waste management.
Recycling Extruder Overview
Modern recycling extruders are essential for converting plastic waste into reusable materials, significantly aiding in waste reduction and sustainability. These machines are a cornerstone of the mechanical recycling process, which can significantly enhance the value of plastic waste by reshaping it into useful products. Extrusion, a pivotal process in the recycling industry, transforms shredded plastic into new forms by heating and shaping it.
An extruder comprises key components including a motor, a worm screw, and a heated sheath that processes plastic materials. Unlike simple melting methods, extrusion allows for better control of the melting temperature, preventing the burning of plastics and ensuring a higher quality end product. This control is crucial for producing uniform, high-quality recycled plastics that can be used in a variety of applications.
Understanding the basic components and process of extrusion allows us to appreciate the technological advancements that make modern recycling extruders so effective. These machines not only enhance the recycling process but also contribute to a more sustainable and efficient way of handling plastic waste.
Types of Recycling Extruders

The main types of recycling extruders are single screw extruders and twin screw extruders. These two types form the backbone of plastic recycling, each with unique features and applications. Single screw extruders are commonly used for the recovery of scrap materials, effectively processing them to recover usable plastics.
On the other hand, twin screw extruders combine traditional design aspects with innovative engineering technologies for enhanced performance, making them highly versatile. New recycling extruders are suitable for handling highly contaminated and heavily printed recycling, including all end-of-life thermoplastics.
This versatility makes them invaluable in the recycling process, as they can manage a wide variety of plastic waste, including post-industrial plastics and other recyclables. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right extruder for specific recycling needs.
Single Screw Extruders
Single screw extruder are commonly used for the recovery of scrap materials in recycling. Their design allows for efficient melting and shaping of plastics, making them ideal for recycling applications. These extruders can effectively process scrap materials to recover usable plastics, contributing significantly to the production of high-quality recycled products.
The efficiency of single screw extruders in melting and shaping plastics makes them a preferred choice in various recycling processes. Their ability to produce uniform, high-quality recycled plastics ensures that the end products meet industry standards and are suitable for a wide range of applications.
Twin Screw Extruders
Twin screw extruders combine traditional design aspects with innovative technologies for enhanced performance. The MD Twin screw extruder series, for instance, is specifically designed for the regranulation of PVC, showcasing its tailored applications. These extruders can handle a wide variety of PVC scrap, including both rigid and flexible forms, making them highly versatile.
The versatility of twin screw extruders allows them to manage a diverse range of plastic waste, including heavily contaminated materials. This adaptability makes them an essential tool in the recycling process, ensuring that a broad spectrum of waste plastics can be efficiently processed and recycled into high-quality products.
How Recycling Extruders Work
The recycling process using extruders begins with the shredding of plastic waste into smaller pieces to facilitate easier melting. This initial step is crucial as it prepares the plastic for the subsequent melting phase. During the melting phase, rotating screws in the extruder apply heat and pressure to transform the plastic into a molten state.
As the plastic melts, the extruder not only transforms it into a molten state but also removes air bubbles and contaminants, enhancing the quality of the final recycled product. This continuous operation streamlines the processing of plastic waste, making the recycling process more efficient. Impurities in the melted plastic are filtered out using mesh filters to ensure the material is clean before shaping.
After filtration, the molten liquid plastics and liquids are extruded through a die, creating new forms such as pellets or sheets based on the design of the die. Cooling systems are then essential to solidify the shaped plastic and ensure it retains its form. This step-by-step process highlights the efficiency and effectiveness of recycling extruders in transforming plastic waste into valuable, reusable materials.
Advantages of Using Recycling Extruders

Mechanical recycling with recycling extruders has lower environmental burdens than virgin material production. This cost-effective method significantly enhances production by converting plastic waste into uniform, high-quality pellets. Factors that affect the cost of mechanical recycling include:
- Collection fees
- Transportation fees
- Process efficiency
- Material type
- Contamination degree.
The environmental and economic benefits of using recycling extruders are substantial. Recycling extruders lower operational costs by reducing the need for new raw materials. This cost efficiency is directly associated with the purity and type of material processed, making recycling extruders a financially viable option for managing plastic waste.
Recycling extruders not only offer economic benefits but also improve the quality of recycled plastics. Their advanced filtration systems ensure that impurities are effectively removed, resulting in high-quality recycled products that meet industry standards.
Enhanced Efficiency
Modern recycling extruders are equipped with advanced features like thermal temperature control systems and automated feeding mechanisms, enhancing their efficiency. These features allow for better control over the recycling process, reducing downtime and increasing overall throughput.
These advanced features play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of plastic waste processing. Reducing downtime and increasing throughput, recycling extruders make the recycling process efficient and effective, promoting a more sustainable way of managing plastic waste.
Improved Product Quality
Recycling extruders help in effectively filtering impurities, which leads to higher quality recycled plastic products. This process ensures uniform melt processing, contributing to improved material consistency, which is crucial for producing high-quality products.
Overall, the use of recycling extruders significantly elevates the product quality of recycled plastics, making them safer and more effective for various applications. This improvement in product quality ensures that recycled plastics can be used in a wide range of industries, meeting stringent quality standards.
Cost-Effectiveness
Investing in recycling extruders can lead to long-term savings by reducing the need for new raw materials. These savings from reduced raw material expenses contribute to overall lower operational costs for recycling facilities.
The cost-effectiveness of recycling extruders significantly impacts the financial feasibility of plastic recycling processes. These machines make recycling more affordable, ensuring that plastic recycling is both environmentally beneficial and economically viable.
Key Features of Modern Recycling Extruders
Modern recycling extruders are designed with features that enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. Factors that influence the cost of a plastic extruder include:
- The material processed
- Quality of parts
- Length of screw
- Downstream equipment
- Special accessories
These advanced features ensure that recycling extruders can handle a wide range of plastic waste, including post-industrial plastics and other recyclables. These machines enhance productivity and efficiency, playing a crucial role in the recycling process and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Advanced Control Systems
PLC electricity control systems in extruders enable precise operations, including automated start and stop functionalities. These control systems also offer features like automatic overload protection to enhance the safety and efficiency of the extrusion process.
PLC electric control systems include functionalities like start, stop, forward rotation, and automatic overload protection. These advanced control systems ensure that power recycling extruders operate smoothly and efficiently, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the recycling process.
Jam-Free Operation
Moveable hoppers in modern extruders facilitate smooth material sorted sorting feeding, thereby minimizing the risk of jamming. Moveable hoppers in recycling extruders prevent jams and significantly reduce vibrations during operation.
Coupling-connected transmissions in extruders help in reducing vibration, which further aids in maintaining consistent operation. These features ensure that recycling extruders operate smoothly and efficiently, contributing to a more effective recycling process.
Applications of Recycled Plastics
Recycled plastics can be used to create a variety of products, including:
- Pipes
- Window and door profiles
- Technical profiles
- Pellets
- Medical devices
The versatility of recycled plastics makes them suitable for a wide range of recyclable applications, contributing to a circular economy and reducing the reliance on virgin polymers while promoting the reuse of materials and polymer.
For instance, CPM Extricom Extrusion has developed solutions to recycle PET plastic, allowing the production of food-grade materials from recycled milk bottles. This innovation highlights the potential of recycled plastics to meet stringent quality standards, including their chemical composition, making them suitable for applications such as food packaging and containers.
STABILO International exemplifies the application of recycled plastics by producing pens made from recycled materials, emphasizing sustainability in product design. These examples demonstrate how recycled plastics can be integrated into various industries, promoting sustainability and reducing plastic waste, which is produced from these innovative practices.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Foam Industrial has significantly increased its recycling capabilities, now processing around 14,000 tons of LDPE film annually with the help of a recycling extruder. This success story highlights the effectiveness of recycling extruders in managing large volumes of plastic waste, contributing to a more sustainable recycling process involving polyethylene.
TenCate Grass implemented a shredder-extruder recycling machine to manage waste from its Fibres and Fabrics production in the Netherlands. This implementation showcases how recycling extruders can be integrated into existing production processes to create a waste-free production cycle.
Arexim, a plastics processor in Bulgaria, utilizes shredder-extruder technology to create a waste-free production cycle. These real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of recycling extruders in managing plastic waste and improving sustainability.
These successful implementations highlight the positive impact of recycling extruders on sustainability and the management of plastic waste.
Summary
Recycling extruders play a crucial role in transforming plastic waste into valuable, reusable materials. By enhancing the efficiency of the recycling process and improving the quality of recycled plastics, these machines contribute significantly to sustainability and waste reduction. The advanced features of modern recycling extruders, such as advanced control systems and jam-free operation, make them indispensable in the recycling industry.
The applications of recycled plastics are vast, ranging from everyday items like pens to specialized products like food-grade materials. Real-world success stories further illustrate the effectiveness and benefits of recycling extruders. By investing in this technology, we can move towards a more sustainable future, reducing our reliance on virgin plastics and minimizing plastic waste.
]]>