Plastic extrusion is one of the most common processes of manufacturing plastic materials. It is fast and efficient, which is perfect for making pipes, tubes, sheets, and profiles. Have you ever wondered how plastic material components having uniform cross-sections are manufactured?
In this blog, we will describe plastic extrusion along with how the process works, its materials, different types of extrusion methods, industrial applications, and the numerous advantages plastic extrusion offers.

1) What is Plastic Extrusion?
“Plastic extrusion is a particular method of manufacturing products in a continuous form, including pipes, tubes, and sheets, by melting plastic granules and extruding them through a specially designed die.”
Well, it starts with feeding raw plastic materials in the form of thermoplastic granules into a heated barrel, where they are heated, blended, and drained through a die with a huge rotating screw. It then cools and solidifies as it leaves the die.
This method is used widely since it enables faster production, exceptional precision in quality and a range of options in design. And, it works best for the production of long and homogeneous plastic goods used in construction, automotive, and packaging industries.
2) How the Plastic Extrusion Process Works
There are a number of key steps in the extrusion that create desired products out of plastic granules. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
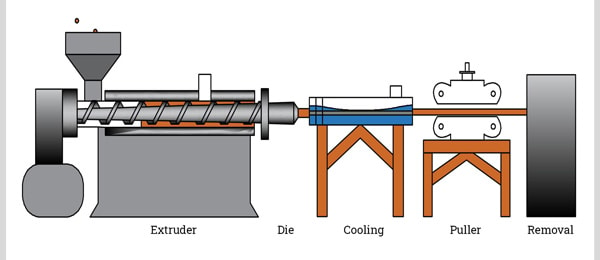
Step 1) Feeding the Hopper
Plastic extrusion begins with raw thermoplastic material in the form of pellets or granules, which is fed into a storage unit, known as a hopper or feed throat. The hopper stores the material as well as regulates its flow into the machinery.
Step 2) Melting Inside the Barrel
The material shifts from the hopper into a long, heated barrel. Inside, a rotating screw pushes the plastic forward. As the plastic moves, it is heated to the required temperature by the electric heaters mounted on the barrel. Also, friction and pressure assist in evenly plastic the melt. And finally, polymer melt happens.

Step 3) Shaping Through the Die
At the die, which is a custom-made mesh-shaped screen pack/breaker plate, the molten material is forced out. As it is pushed out through the die, the plastic acquires the form of the die, which can be round, square, hollow, and the like.
Step 4) Cooling system and solidifying
The extruded plastic is transferred to a cooling chamber, which is either a water bath or an air-cooled chamber ( or drawn through several sets of nip rollers). These methods assist the plastic in cooling down and keep its new shape. For hollow shapes like pipes, vacuum sizing tanks help in sustaining the shape.
Step 5) Cutting to length or rolling process
As a last step, the cooled plastic is either in specific lengths or rolled in the case of sheets or films to make it easier to store and transport the final product.
3) Types of Plastic Extruder
As with any industrial procedure, plastic extrusion has different methods and techniques tailored to different products. The types of plastic extrusion machines include:
i) Sheet film extrusion

These methods aid in the production of plastic sheets and films. Flat dies are utilised, and the extrudates are cooled by means of chill rolls.
- Sheet Extrusion sheet thickness: thicker than 10 mils or 0.25 mm.
- Film extrusion: thinner than 10 mils and utilised in packaging films, garbage bags, etc.
ii) Pipe and Tube Extrusion
This method employs a circular die through which the plastic is extruded and cooled in a vacuum sizing tank. It is perfect for pipes, tubes, straws, and conduits.

iii) Profile Extrusion
These are utilised for producing plastic products with specialised or tailored cross-sections. Such products include window frames, seals, gaskets, and trims for different industrial needs.

iv) Co-Extrusion
In this method, two or more substances are processed through the same die. This technique enables the production of a single item with different layers of plastics possessing disparate characteristics, for instance, a protective barrier, pigment, or elasticity.
v) Blown Film Extrusion
It is a method for producing thin plastic films. While still in a molten state, the plastic is extruded and then blown up like a balloon to be further stretched. This method is employed in grocery bags, shrink wrap, and food packaging films.

4) Common Thermoplastics Used in Extrusion
Not every type of plastic can be extruded. The raw materials utilised in thermoplastics are best-suited for extrusion because these types of plastic can be melted and hardened without dire consequences.

The following materials are commonly used:
- PVC (rigid Polyvinyl Chloride): Used in pipes and profiles and serves as cable insulation. Can be flexible or rigid depending on formulation.
- PE (Polyethene): Found in tubing, films, and sheets. Comes in LDPE, HDPE, and LLDPE.
- PP (Polypropylene): Lightweight and tough. Used in automotive, packaging, and household goods.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Impact-resistant and rigid, used in construction and consumer goods.
- PS (Polystyrene): Used in lighter rigid goods, for example, trays, containers, and packaging.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Flexible and abrasion-resistant; used for seals and cables, and medical tubing extrusion.
All materials mentioned before differ in specific melting points, flow characteristics, and applications.
5) Key Applications of Plastic Extrusion
The extrusion of plastic serves various functions in life. Consider these as the most important uses in which plastic extrusion serves.

- Construction Industry: Thermoplastics are durable and highly customizable in design, which makes these packaging materials perfect for window frames, pipes, wall panels, trims, and insulation components.
- Packaging Industry: The blown film extrusion process make plastic used as film containers, shrink wraps, and food containers.
- Automotive Sector: Commonly extruded items include weather seals, door edge guards, cable insulation, and dashboard profiles.
- Electrical and Electronics: Switch housing profiles, as well as conduits and wires, are insulated with extruded plastics ( what is extruded plastic? Well, the plastic which is being extruded via a twin screw extruder is termed as extruded plastics).
- Consumer Products: Extruded plastics are also utilised in garden hoses, curtain rails, and various plastic furniture components, as well as tool handles.
- Medical and Healthcare: For precision and hygiene, medical-grade plastic extrusion is utilised to manufacture tubing, IV lines, and catheter components.
6) Advantages of Plastic Extrusion
The advantages plastic continuous extrusion offers make it suitable for industrial and mass production purposes:
Ideal for large quantity production: Plastic extrusion provides a low cost per unit of production for large quantities due to the continuous sheeting production method used.
Diverse production possibilities: Use of custom-made dies for extrusion allows the production of different shapes and thin films with ease.
Material efficiency: Waste from the extrusion process is often recyclable and can be remelted for reuse, thus cutting costs and increasing sustainability.
Increased speed and reduced need for staff: Reduced need for staff is a result of increased automation in modern extrusion lines, which are capable of mass production at high speeds.
Customisation Opportunities: You can easily add colours, textures, uv inhibitors, flame retardants, or other additives, as well as multi-layered profiles.
Lower pressure Tooling Costs: Extrusion typically has a lower cost and shorter turnaround time for jacketing tooling when compared with plastic injection molding.
7) Limitations and Challenges
Every process has limitations, and with extrusion, these are the most notable:

Constraints of Basic Profiles: Uniform cross-sectioned components that are lengthy are best produced by plastic extrusion. Moreover, it is limited in generating a detailed or intricate desired shape.
Material Shrinkage: Deformation or dimensional inaccuracies can occur due to some plastics shrinking non-uniformly during the cooling process.
Surface Defects: Poor design of the die or inconsistent cooling can lead to surface imperfections, roughness, waviness, and discolouration.
Not All Plastics can be used: Due to the degradation or a loss of strength, certain plastics can undergo degradation at high temperatures during the extrusion process. So, the choice of materials is restricted.
High Setup Cost: For small-volume custom jobs, the process becomes less desirable due to the high creation and adjustment costs of the dies.
– Less Accuracy Compared to Other Methods: While using extrusion, it is less accurate when compared to injection molding and CNC, particularly for small, intricate, and tightly toleranced parts.
8) Plastic Extrusion vs. Injection Molding
While both methods are used in the plastic manufacturing process, they serve different purposes:
| Feature | Extrusion | Injection Molding |
| Shape Type | Continuous profiles | Individual parts or components |
| Process Duration | Continuous | Cyclical |
| Product Examples | Pipes, sheets, films, cables | Gears, bottle caps, containers |
| Tooling Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Production Volume | High-volume manufacturing process for uniform parts | Medium to high for custom parts |
9) Plastic Extrusion vs. Aluminium Extrusion
Though both processes are called “extrusion,” they differ significantly in materials and techniques.
| Feature | Plastic Extrusion | Aluminum Extrusion |
| Material Type | Thermoplastics | Aluminum billets |
| Melting Point | Low (typically 160–260°C) | High (over 500°C) |
| Die Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Cycle Time | Fast and continuous process | Slower, batch-based |
| Strength of Product | Lower | High strength |
| Applications | Tubes, films, profiles | Structural parts, heat sinks, frames |
Plastic extrusion is ideal for flexibility, low cost, and insulation properties. Aluminum extrusion is better suited for strength, rigidity, and durability in structural applications.
10) Low-Volume Custom Plastic Extrusion (3ERP Spotlight)
If you require mass production, Faygo Union is a reliable rapid manufacturing provider with custom solutions for Customized adaptation machines.
This is especially useful for:
- Prototyping
- Testing the market with new offerings
- Running limited production in a tight timeframe
With advanced extrusion equipment, Faygo Union customises and manufactures as expertly as they promise. Our flexible production and fast delivery enable us to expertly partner with engineering teams and startups. You can get in touch with us right now!
11) Conclusion
Extrusion technology has brought greater convenience and possibilities to human life. It enables the efficient production of a wide range of plastic products. We also use extrusion to produce a wide range of everyday items, such as building materials and medical catheters, as well as specialized plastic packaging. This method, while ensuring quality, offers rapid and cost-effective production, making it a crucial step in the history of industrial development.




